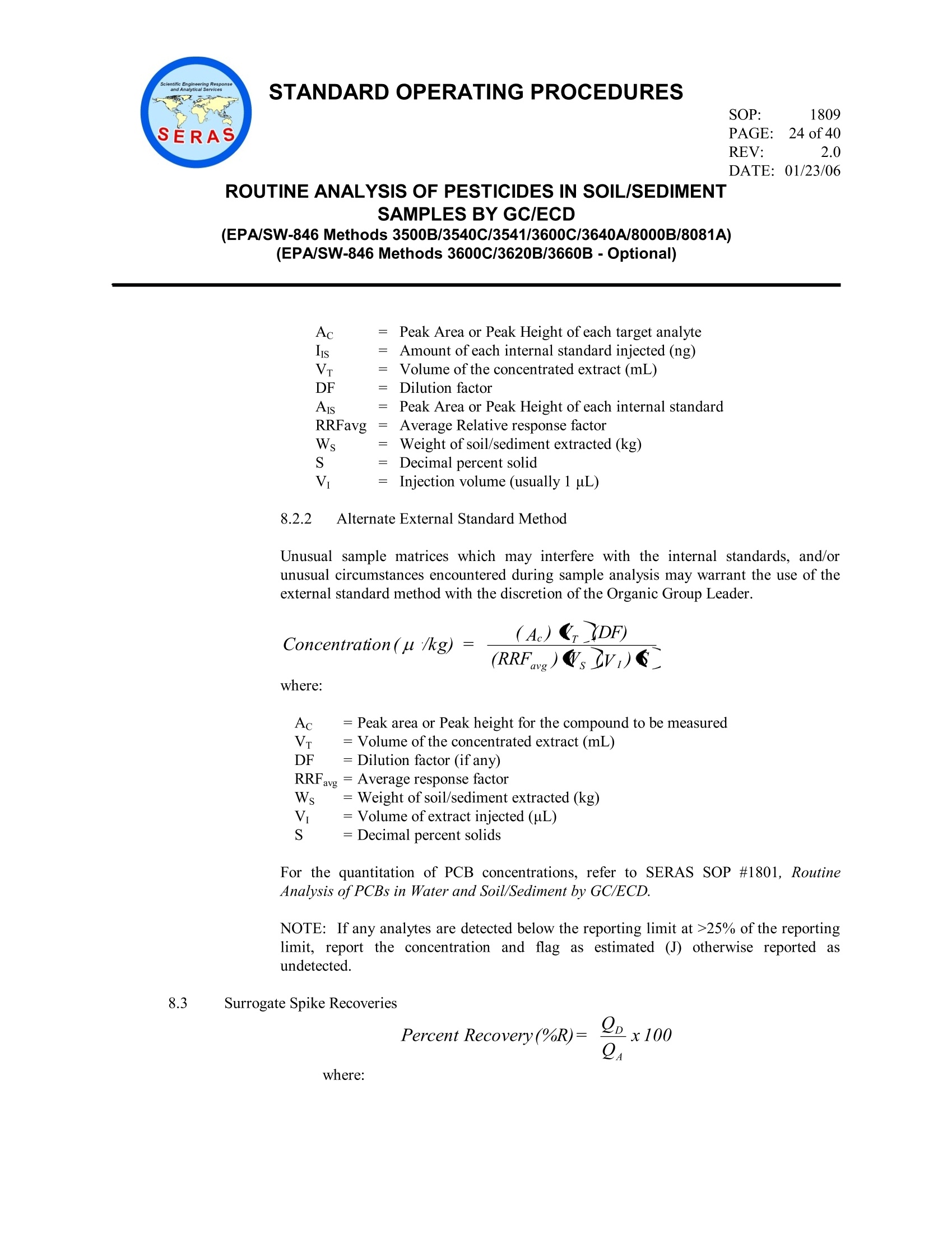
方案详情
文
This standard operating procedure (SOP) is applicable to the determination of organochlorine pesticides
with the possible presence of polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) or toxaphene in soil/sediment matrices
using a gas chromatograph (GC) with a narrow-bore fused silica column and an electron capture detector
(ECD). This SOP is based on Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) Methods
SW846/3500B/3540C/3541/8000B/8081A and those requirements set forth in the latest approved version
of the National Environmental Laboratory Accreditation Committee (NELAC) Quality Systems section.
Gel permeation chromatography [GPC] cleanup is required and is based on EPA/SW-846 Methods
3600C/3640A. Extracts may be subjected to optional cleanup procedures (florisil, tetrabutylammonium
[TBA] sulfite or activated copper powder) based on EPA/SW-846 Methods 3600C/3620B/3660B. The
compounds of interest and typical reporting limits (RLs) in soil/sediment matrices are found in Table 1,
Appendix A.
方案详情

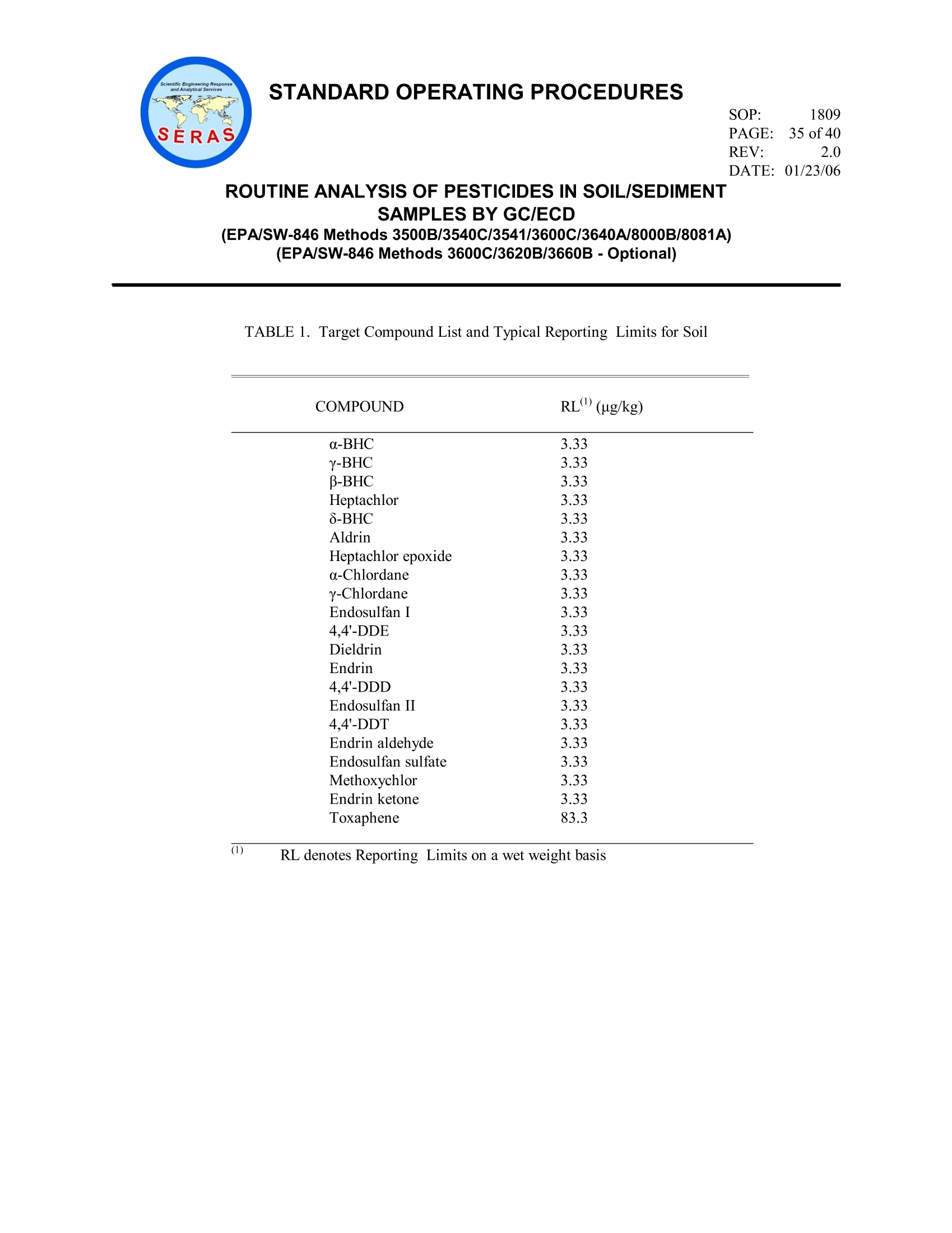
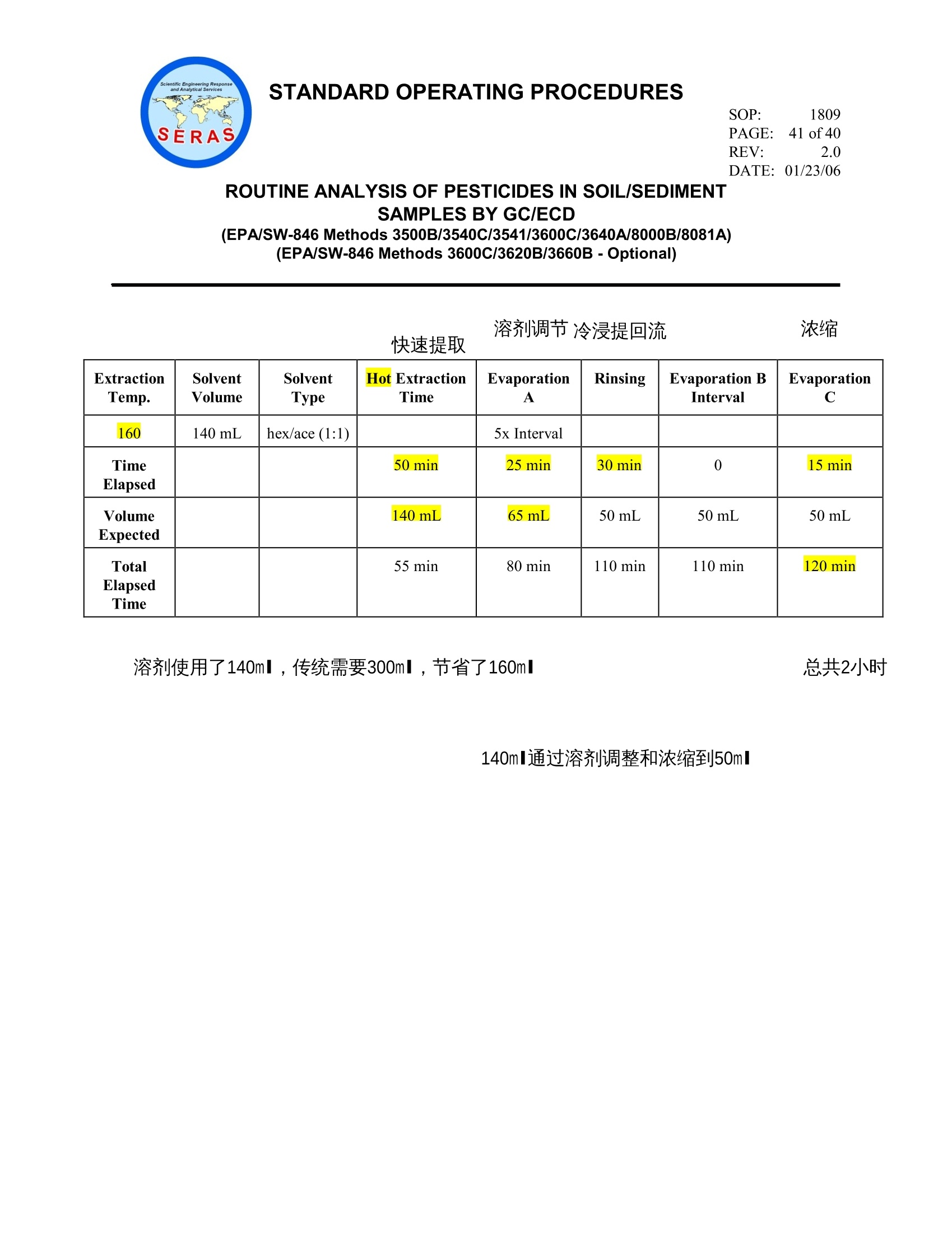
STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURESPAGE: 1 of 40DATE: 01/23/06(EPA/SW-846 Methods 3500B/3540C/3541/3600C/3640A/8000B/8081A)(EPA/SW-846 Methods 3600C/3620B/3660B -Optional) STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURESPAGE: 2 of 40DATE: 01/23/06 SOP: 1809 REV: 2.0 ROUTINE ANALYSIS OF PESTICIDES IN SOIL/SEDIMENTSAMPLES BY GC/ECD CONTENTS 1.0 SCOPE AND APPLICATION* 2.0 METHOD SUMMARY 3.0 SAMPLE PRESERVATION,CONTAINERS,HANDLING, AND STORAGE 3.1 Sample Storage 3.2 Holding Time 4.0 INTERFERENCES AND POTENTIAL PROBLEMS 5.0 EQUIPMENT/APPARATUS 6.0 REAGENTS 7.0 PROCEDURES 7.1 Sample Preparation and Extraction 7.2 Total Solids 7.3 Gel Permeation Chromatography Cleanup 7.4 Florisil Cleanup 7.5 Tetrabutylammonium (TBA)-Sulfite Cleanup 7.6 Copper Cleanup 7.7 GC/ECD Conditions 7.8 Retention Time Windows 7.8.1 Alternate Retention Time Window Determination 7.9 Standard and Sample Analysis 7.9.1 Pesticide Analysis (excluding toxaphene) 7.9.2 Toxaphene Analysis 7.9.3 PCB Analysis SOP: 1809 REV: 2.0 ROUTINE ANALYSIS OF PESTICIDES IN SOIL/SEDIMENTSAMPLES BY GC/ECD (EPA/SW-846 Methods 3500B/3540C/3541/3600C/3640A/8000B/8081A) (EPA/SW-846 Methods 3600C/3620B/3660B-Optional) CONTENTS (cont) 7.10 Evaluation of Chromatograms 7.10.1 Standard/Sample Chromatograms 7.10.2 Pesticide Identification 7.11 Sample Dilution 8.0 CALCULATIONS 8.1 Reporting Limit for Soil 8.2 Sample Concentration for Soil 8.2.1 Internal Standard Method 8.2.2 Alternate External Standard Method Surrogate Spike Recoveries Matrix Spike Recoveries 8.5 Laboratory Control Sample Recoveries 9.0 QUALITY ASSURANCE/QUALITY CONTROL 9.1 Holding Time 9.2 Identification of Target Compounds 9.3 GC Column Performance 9.4 Initial Calibration for Target Compounds and Surrogates 9.5 Continuing Calibration for Target Compounds and Surrogates 9.6 Retention Time Windows 9.7 Analytical Sequence 9.8 Method Blank and Laboratory Control Sample 9.9 Surrogate Recoveries 9.10 Internal Standard 9.11 Matrix Spike and Matrix Spike Duplicate Analysis 9.12 Initial Demonstration of Capability 9.13 Dilution Analysis 9.14 Reporting Limit 9.15 Method Detection Limit Studies 9.16 Nonconformance Memo SOP: 1809 REV: 2.0 ROUTINE ANALYSIS OF PESTICIDES IN SOIL/SEDIMENTSAMPLES BY GC/ECD CONTENTS (cont) 10.0 DATA VALIDATION 11.0 HEALTH AND SAFETY 12.0 REFERENCES* 13.0 APPENDICES A -Table* B -Figures C -Soxtherm Extractor Operating Conditions * These sections affected by Revision 2.0. SOP: 1809 PAGE: 4 of 40 REV: 2.0 DATE: 01/23/06 ROUTINE ANALYSIS OF PESTICIDES IN SOIL/SEDIMENTSAMPLES BY GC/ECD (EPA/SW-846 Methods 3500B/3540C/3541/3600C/3640A/8000B/8081A) (EPA/SW-846 Methods 3600C/3620B/3660B-Optional) 1.0 SCOPE AND APPLICATION This standard operating procedure (SOP) is applicable to the determination of organochlorine pesticideswith the possible presence of polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) or toxaphene in soil/sediment matricesusing a gas chromatograph (GC) with a narrow-bore fused silica column and an electron capture detector(ECD). This SOP is based on Environmental ProtectionAgency(EPA) MethodsSW846/3500B/3540C/3541/8000B/8081A and those requirements set forth in the latest approved versionof the National Environmental Laboratory Accreditation Committee (NELAC) Quality Systems section.Gel permeation chromatography [GPC] cleanup is required and is based on EPA/SW-846 Methods3600C/3640A. Extracts may be subjected to optional cleanup procedures (florisil, tetrabutylammonium[TBA] sulfite or activated copper powder) based on EPA/SW-846 Methods 3600C/3620B/3660B. Thecompounds of interest and typical reporting limits (RLs) in soil/sediment matrices are found in Table 1,Appendix A. This method may not be changed without the expressed approval of the Organic Group Leader, theAnalytical Section Leader and the Quality Assurance Officer (QAO). Only those versions issued throughthe SERAS document control system may be used. Modifications made to the procedure due tointerferences in the samples or for any other reason must be documented in the case narrative and on anonconformance memo. 2.0 METHOD SUMMARY Approximately 30 grams (g) of a soil/sediment sample mixed with 30 g of anhydrous sodium sulfate isextracted with 140 milliliters (mL) of 1:1 acetone/hexane using a Soxtherm extractor for 2 hours or 300milliliters (mL) of 1:1 acetone/hexane using a Soxhlet extractor for 16 hours. The extract is concentratedto 10 mL, 60 mL of hexane is added as an exchange solvent, and the extract is concentrated to a finalvolume of 5 mL. The extracts are analyzed for pesticides using GC/ECD. Second column confirmation isrequired for the confirmation of single component pesticides but not required for multi componentcompounds such as PCBs or toxaphene analysis. 3.0 SAMPLE PRESERVATION,CONTAINERS, HANDLING, AND STORAGE 3.1 Sample Storage Samples should be collected in wide mouth 8-ounce (oz) amber glass containers with a Teflonlined caps. From the time of collection until after analysis, extracts and unused samples must beprotected from light and refrigerated at 4±2 degrees Celsius (C) for the periods specified bySERAS Task Leader (TL) and/or the Work Assignment Manager (WAM) for the project. Samples and sample extracts must be stored separately from standards in an atmosphere free ofall potential contaminants. SOP: 1809 REV: 2.0 ROUTINE ANALYSIS OF PESTICIDES IN SOIL/SEDIMENTSAMPLES BY GC/ECD (EPA/SW-846 Methods 3500B/3540C/3541/3600C/3640A/8000B/8081A) (EPA/SW-846 Methods 3600C/3620B/3660B-Optional) 3.2 Holding Times Extraction of soil/sediment samples shall be completed within 7 days from date of collection, andanalysis completed within 40 days after sample extraction. 4.0 INTERFERENCES AND POTENTIAL PROBLEMS Solvents, reagents, glassware, and other sample processing hardware may yield artifacts and/orinterferences in the sample extracts for analysis. All of these materials must be demonstrated to be freefrom interferences under the conditions of the analysis by analyzing laboratory reagent blanks on a routinebasis. Interferences co-extracted from the samples may vary considerably from sample to sample.Cleanup procedures may be necessary if the extract contains analytes that interfere with quantitation orpeak separation. Phthalate esters are present in many types of products commonly found in the laboratory. Some plastics,in particular, must be avoided because phthalates are commonly used as plasticizers and are easilyextracted from plastic materials.5.Serious phthalate contamination may result at any time if consistentquality control is not practiced. Soap residue on glassware may cause degradation of certain analytes.This problem is especiallypronounced with glassware that may be difficult to rinse.These items should be hand-rinsed verycarefully to avoid this problem. Elemental sulfur is encountered in many sediment samples such as marine algae and some industrialwastes. Sulfur will be quite evident in gas chromatograms obtained from ECDs. If the GC is operated atthe normal conditions for pesticide analysis, the sulfur interference can completely mask the region fromthe solvent peak through the aldrin peak. Three techniques, gel permeation chromatography (GPC)cleanup, activated copper powder, or tetrabutylammonium (TBA) sulfite for the elimination of sulfur maybe used. Florisil cleanup may be used to reduce matrix interferences caused by polar compounds. 5.0 EQUIPMENT/APPARATUS The following equipment/apparatus is required: Soxthermextractor, including its accessories (e.g., extraction flask, sample holding vessel, chiller,etc.), manufactured byGerhardt or equivalent Waters GPC instrument or equivalent Soxhlet extractor, 40 millimeter (mm) inner diameter (ID), with 500-mL round bottom flask, fits45/50 condenser SOP: 1809 REV: 2.0 DATE: 01/23/06 ROUTINE ANALYSIS OF PESTICIDES IN SOIL/SEDIMENT SAMPLES BY GC/ECD (EPA/SW-846 Methods 3500B/3540C/3541/3600C/3640A/8000B/8081A) (EPA/SW-846 Methods 3600C/3620B/3660B -Optional) ● Teflon boiling chips, approximately 10/40 mesh, rinsed three times with methylene chloride Spoon and/or spatula, stainless steel or Teflon Glass container(s) Glass wool, Pyrex baked at 400℃ for 2 hours Kuderna-Danish (K-D) apparatus, consisting of a 10-mL graduated concentrator tube, 500-mLevaporation flask, and three-ball macro Snyder column Water bath, heated with concentric ring cover, capable of maintaining temperature within ±2°C. Thebath should be used in a hood. Disposable glass pasteur pipettes Nitrogen evaporation device, equipped with a water bath that can be maintained at 35-40℃ (N-Evapby Organomation Associations Model Number 111 or equivalent) TurboVap concentrator, with concentrator cells and racks Clean Bath solution, for use in TurboVap II concentrator Drying oven Desiccator Vials and caps, 2 mL for GC autosampler Vials,4-mL, for GPC cleanup Test tubes with screw caps, 25 mL Gas chromatograph- An analytical system complete with GC and all required accessories includingsyringes, autosampler, analytical columns, gases, dual electron capture detector, and data system. Adata system is required for measuring peak areas or peak heights and recording retention time. RTX-XLB fused silica capillary column, 30 meter (m) x 0.32 mm ID, 0.50 micron (um) filmthickness or equivalent Rtx - CLPesticides fused silica capillary column, 30 m x 0.32 mm ID, 0.50 um film thickness orequivalent SOP: 1809 REV: 2.0 ROUTINE ANALYSIS OF PESTICIDES IN SOIL/SEDIMENTSAMPLES BY GC/ECD (EPA/SW-846 Methods 3500B/3540C/3541/3600C/3640A/8000B/8081A) (EPA/SW-846 Methods 3600C/3620B/3660B-Optional) Cellulose/Fiberglass thimbles , pre-washed with methylene chloride Teflon filters, 0.45um, for filtering extracts for GPC cleanup (Gelman Acrodisc CR or eguivalent) Florisil cartridge, 12 mL tube (Supelco CAT#57155 or equivalent) Visiprap SPE Vacuum manifold, 12 port or equivalent Valve liners, disposable or equivalent Syringes, various microliters (uL) volumes, for spiking and preparation of standards Micro syringes, 10 pL and larger, 0.006 inch ID needle Class "S" weights for calibrating balance Analytical balance, capable of accurately weighing±0.01 g Volumetric flasks, Class A, various volumes ranging from 5 to 500 mL 6.0 REAGENTS Sodium Sulfate, anhydrous granular reagent grade, heated at 400 C for four hours, cooled in adesiccator, and stored in a glass bottle. Hexane, pesticide residue analysis grade or equivalent Acetone, pesticide residue analysis grade or equivalent Methanol, pesticide residue analysis grade or equivalent 2-Propanol, pesticide residue analysis grade or equivalent Methylene chloride, pesticide residue analysis grade or equivalent Tetrabutylammonium sulfite solution -Prepare by dissolving 3.39 g of tetrabutylammoniumhydrogen sulfate in 100 mL of reagent wateterr.. Extract this solution three times with 20 mLportions of hexanes to remove any impurities. Discard the hexane layer and add 25g of sodiumsulfite to the aqueous layer. Store this solution at room temperature. Copper powder, activated, commercially available 1SOP: 1809 REV: 2.0 ROUTINE ANALYSIS OF PESTICIDES IN SOIL/SEDIMENTSAMPLES BY GC/ECD (EPA/SW-846 Methods 3500B/3540C/3541/3600C/3640A/8000B/8081A) (EPA/SW-846 Methods 3600C/3620B/3660B-Optional) Pesticide InternalilStandard Solution Prepare a solution containing 4.4'-Dibromooctafluorobiphenyl,4,4'--Dibromobiphenyl,and 3,3',4,4'-Tetrabromobiphenylvlatconcentration of 5 microgram/milliliter (ug/mL) in hexane. Stock Pesticide Calibration Standard, 200 milligrams/liter (mg/L), commercially available Working Pesticide Calibration Standards - Prepare a minimum of five concentration levels at 20,50, 100, 200, 500 micrograms/liter (ug/L). Each calibration standard must contain all of thecompounds listed in Table 1, Appendix A, contain the two surrogates at the same concentrationsasthe calibration standards, and contain the pesticide internal standard compoundsscatconcentration of 100 ug/L. Add 20pL of the 5 ppm IS to 1mL for all standards. Stock Pesticide Surrogate Standard, 200 mg/L, commercially available. Working Pesticide Surrogate Solution - Prepare a solution containing decachlorobiphenyl(DCBP) and 2,4,5,6-tetrachloro-meta-xylene (TCMX)at a concentration of 2 ug/mL in methanolor acetone. Stock Pesticide Matrix Spike (MS) Solution, 100/200 mg/L, commercially available, source mustbe independent of the calibration standards Working Pesticide MS Solution -Prepare a spiking solution in methanol or acetone that containsthe pesticides at the concentrations specified below: gamma-BHC 1.25 pg/mL Heptachlor 1.25 ug/mL Aldrin 1.25 ug/mL Dieldrin 2.50 pg/mL Endrin 2.50 ug/mL 4,4'-DDT 2.50 pg/mL Stock Toxaphene Calibration Standard, 1000 milligrams/liter (mg/L), commercially available Working Toxaphene Calibration Standards - Prepare at a minimum of five concentration levelsat 0.5, 1,2, 5, 10 ug/mL. Each calibration standard must contain toxaphene, the two surrogatesat concentrations of 20, 50,100,200,500 ug/L, and the pesticide internal standard compounds atconcentration of 100 ug/L. Stock Toxaphene MS Solution,1000 mg/L, commercially available, source must be independentof the calibration standards SOP: 1809 REV: 2.0 DATE: 01/23/06 ROUTINE ANALYSIS OF PESTICIDES IN SOIL/SEDIMENTSAMPLES BY GC/ECD (EPA/SW-846 Methods 3500B/3540C/3541/3600C/3640A/8000B/8081A) (EPA/SW-846 Methods 3600C/3620B/3660B-Optional) Working Toxaphene MS Solution- Prepare a spiking solution in methanol or acetone thatcontains the toxaphene at 20 mg/L. PCB Calibration Standards, refer to SERAS SOP #1801, Routine Analysis ofPCBs in Water andSoil/Sediment by GC/ECD. Stock Resolution Check Mixture, 1 to 10 mg/L, commercially available Working Resolution Check Solution - Prepare a mixture of pesticides in hexane or methanol atthe concentrations in nanograms/milliliter (ng/mL) listed below from the 1-10 mg/L stockresolution check solution. Spike 20pL of 5ppm IS to a 1mL solution. Endosulfan I 20 ng/mL 4,4'-DDE 40 ng/mL Dieldrin 40 ng/mL Endosulfan sulfate 40 ng/mL Endrin ketone 40 ng/mL Methoxychlor 200 ng/mL Tetrachloro-m-xylene 40 ng/mL Decachlorobiphenyl 40 ng/mL Stock Performance Evaluation Mix (PEM), 1 to 25 mg/L, commercially available Working PEM Solution -Prepare the working PEM in hexane or methanol at the concentrationlevels listed below using the 1-25 mg/L stock PEM solution. Spike 20pL of 5ppm IS to 1 mLsolution. gamma-BHC 20 ng/mL alpha-BHC 20 ng/mL 4,4-DDT 200 ng/mL beta-BHC 20 ng/mL Endrin 100 ng/mL Methoxychlor 500 ng/mL Tetrachloro-m-xylene 40 ng/mL Decachlorobiphenyl 40 ng/mL NOTE:: All of the above mentioned standard solutions must be stored at 4℃ in tightly cappedvials with Teflon liners. SOP: 1809 PAGE: 10 of 40 REV: 2.0 DATE:01/23/06 ROUTINE ANALYSIS OF PESTICIDES IN SOIL/SEDIMENTSAMPLES BY GC/ECD (EPA/SW-846 Methods 3500B/3540C/3541/3600C/3640A/8000B/8081A) (EPA/SW-846 Methods 3600C/3620B/3660B-Optional) NOTE: Premixed certified standards will be stored according to the manufacturer’s documentedstorage requirements.These standards may be kept in storage up to the manufacturer’s statedexpiration date. Once the standard vials are opened, the standards will be stored with minimalheadspace in the freezer for a period not to exceed six months or the manufacturer’s expirationdate, whichever is less. NOTE: All calibration standards, surrogates, internal standards, and spiking solutions will beprepared and documented in accordance with SERAS SOP #1012, Preparation of StandardSolutions and Reagents. 7.0 PROCEDURES 7.1 Sample Preparation and Extraction 1. In a fume hood, place 140 mL of 1:1 acetone/hexanee into a Soxthermextraction vesselscontaining 2 boiling chips. If using Soxhlet extraction, place 300 mL of 1:1 acetone/hexaneinto a 500-mL round bottom flask containing 3 or more clean boiling chips. 2. Transfer the sample container into the fume hood. Open the sample bottle and discard anyforeign objects such as sticks, leaves, and rocks. Mix the sample thoroughly. 3. Calibrate the balance with Class “S” Weights prior to weighing samples or on a daily basiswhen the balance is in use. The balance should be calibrated with a weight that is similar tothe weight used to extract the samples (i.e.,30 g). 4. Weigh approximately 30 g of each sample to the nearest 0.1g into a glass container and adda sufficient amount (approximately 30-100g) of anhydrous granular sodium sulfate. Mixwell. The sample should have a sandy texture at this point. A method blank and lab controlsample (LCS) must be prepared by using 30 g of sand (or baked sodium sulfate) accordingto the same procedure as the samples, at the frequency of one per 20 samples or per batch. 5. Transfer the sample to a pre-cleaned extraction thimble. Place the thimble containingsamples to Soxtherm extraction vessel. For Soxhlet extraction, take a piece of baked glasswool and place it in the Soxhlet extractor so it covers the bottom of the inner diameter. Addsome sodium sulfate to hold the glass wool in place; this will prevent any soil/sediment fromgetting caught and clogging the Soxhlet. Add the blended sample and anhydrous sodiumsulfate into the Soxhlet extractor on top of glass wool and sodium sulfate. 6. Weigh two additional 30 g portions of the sample chosen for spiking to the nearest 0.1 g foruse as a MS/matrix spike duplicate (MSD) at a rate of one per ten samples per project or tenpercent. SOP: 1809 PAGE: 11 of 40 REV: 2.0 DATE:01/23/06 ROUTINE ANALYSIS OF PESTICIDES IN SOIL/SEDIMENTSAMPLES BY GC/ECD (EPA/SW-846 Methods 3500B/3540C/3541/3600C/3640A/8000B/8081A) (EPA/SW-846 Methods 3600C/3620B/3660B-Optional) NOTE: This sample may be specified on the Chain of Custody record for this purpose by theSERAS Task Leader. 7. Add 0.5 mL of the 2 pg/mL surrogate working solution to the method blank, LCS,MS/MSDand all the samples or add sufficient volume to result in a final concentration of 200 partsper billion (ppb) in the final extract. 8.川Add 0.5 mL of the 1.25/2.50 ug/mL pesticide matrix spiking solution to the LCS andMS/MSD or add sufficient volume to achieve a final concentration of 0.125/0.250 mg/L inthe final extract. 9. Attach the extraction vessel to the:SSoxtherm extractor and extract for2hours. TheSoxtherm extraction conditions are specified in Appendix C. For Soxhlet extraction, attachcondenser to the extractor and flask, and extract the sample(s) for 16 hours. NOTE: Care must be taken to supervise the beginning of the extraction to ensure that thecondenser is cooling the evaporating solvent sufficiently to guarantee that the solvent willcondense and continue to extract the sample in a continuous cycle for the entire extraction.Allow the extract to cool after the extraction is complete. 10. If concentrating using a TurboVap apparatus, skip to step 14. Otherwise, assemble a K-Dapparatus by attaching a 10-mL concentrator tube to a 500-mL evaporation flask. Transferthe extract to the K-D concentrator. 11. Add one or two clean boiling chips to the evaporation flask and attach a three-ball Snydercolumn. Place the K-D apparatus on a hot water bath (70 to 75 C) so that the concentratortube is partially immersed in the hot water and the entire lower rounded surface of the flaskis bathed with hot vapor. Add approximately 1 mL of hexane to the top of Snyder column.Adjust the vertical position of the apparatus and the water temperature as required tocomplete the concentration. At the proper rate of distillation, the balls of the column willactively chatter, but the chambers will not flood with condensed solvent. When the apparentvolume of liquid is below 10 mL, add another 60 mL of hexane and evaporate down to below10 mL. Remove the K-D apparatus, and allow it to drain and cool. NOTE::DO NOT ALLOW THE EXTRACT TO GO TO DRYNESS..However, If theextract goes to dryness, document the situation in the extraction log book. 12. Remove the Snyder column; use 1-2 mL of hexane to rinse the flask and its lower joint intothe concentrator tube. Remove the concentrator tube and place it onto the N-Evap preheatedto 35 C. 13. Evaporate the extract to a final volume of5 mL for soil. During evaporation rinse the wall SOP: 1809 REV: 2.0 DATE:01/23/06 ROUTINE ANALYSIS OF PESTICIDES IN SOIL/SEDIMENTSAMPLES BY GC/ECD (EPA/SW-846 Methods 3500B/3540C/3541/3600C/3640A/8000B/8081A) (EPA/SW-846 Methods 3600C/3620B/3660B-Optional) of the concentrator tube with 1-2 mL of hexane. Continue with step 16. NOTE: DO NOT ALLOW THE EXTRACT TO GO TO DRYNESS..However, If theextract goes to dryness, document the situation in the extraction log book. 14. If using the TurboVap concentrator, fill the TurboVap water bath with approximately onegallon of deionized water mixed with 10-15 drops of Clean Bath solution. Set the water bathtemperature at 55 C. 15. Transfer the extract to the concentrator cells in the hood. Begin concentrating by blowing agentle stream of nitrogen into the cells so that no solvent is splashed out. As the solventlevel is reduced, add any remaining extract, rinse the flask with hexane, and add the rinsateto the concentration cel. Once all the extract has been transferred to the concentrator celland the solvent level is well below the 200-mL mark, the flow of nitrogen can be increased tospeed up the concentration. Periodically rinse the cell with hexane. Concentrate the extractbelow 10 mL, add 60 mL of hexane and concentrate it down to a final volume of5 mL. NOTE: DO NOT ALLOW THE EXTRACT TO GO TO DRYNESS.However, If theextractgoes to dryness, document the situation in the extraction log book. 16. Take a 4-mL aliquot of all sample extracts including the method blanks, LCSs, theMS/MSDs from Steps 13 or 15 and proceed to the mandatory GPC cleanup describedprocedure as Section 7.3 and/or optional Florisil cleanup described in Section 7.4, optionalTBA-sulfite cleanup described in Section 7.5 or optional copper cleanup described in Section7.6. Store the remaining extract(s) at 4C±2℃. NOTE::Record the date and clean-up procedure of the applicable samples subjected tocleanup on the extraction log. 7.2 Total Solids The sample aliquots for total solids are weighed in conjunction with the samples for theextraction. The total solids for the MS/MSD is based on the corresponding sample. The blank isassumed to be 100% total solids. Weigh and record (in the % solid log book) an empty aluminum sample dish to the nearest 0.01g.Weigh at least 10.0 g of the soil/sediment into the aluminum dish and record the weight.Preheat the oven to103-105C. Place the aluminum dishes in the oven and record the initialtemperature in the logbook. Determine the percent total solids by drying the sample(s) in anoven that is placed inside of a fume hood overnight. In the morning,record the final temperatureof the oven in the log book. Turn off the oven and allow the dishes to cool in the desiccatorbefore weighing. Concentrations of individual analytes will be reported relative to the dry weight SOP: 1809 PAGE: 13 of 40 REV: 2.0 DATE: 01/23/06 ROUTINE ANALYSIS OF PESTICIDES IN SOIL/SEDIMENTSAMPLES BY GC/ECD (EPA/SW-846 Methods 3500B/3540C/3541/3600C/3640A/8000B/8081A) (EPA/SW-846 Methods 3600C/3620B/3660B-Optional) of the soil or sediment. Calculate the percent total solids using the following equation: Weight of Dried Sample with Dish (g)- Dish Weight (g)%Total Solids= -Weight of Wet Sample with Dish (g)- Dish Weight(g) 7.3 Gel Permeation Chromatography Cleanup 1. Calibrate the GPC instrument by injecting 10 uL of GPC standard (corn oil, bis (2-ethylhexyl) phthalate, methoxychlor, perylene, and sulfur) and eluting it with methylenechloride to establish collection time window to collect the fraction from the beginning ofmethoxychlor peak to the end of perylene peak. 2. When the collection time window has been established , inject a methylene chlorideblank to make sure all calibration components are washed from the column. 3. Before injecting the samples, filter 4 mL of each extract including method blanks, LCSsand MS/ MSDs through acrodisc CR PTFE filter (Gelman, 0.45um) into a clean 4-mLvial. 4. Load the 4-mL vials which contain pre-filtered extracts onto the autosampler and startthe sequence. 5. Collect the cleaned extracts from the fraction collector,transfer to the concentrator tubesand concentrate the extracts to a final volume of 2 mL using TurboVap. NOTE: GPC Pump flow rate is 5.0 mL/minute GPC Run time is 25 minutes 7.4 Florisil Cleanup Florisil cleanup significantly reduces matrix interferences caused by polar compounds. 1. Place one Florisil cartridge into the manifold for each sample extract to be subjected tocleanup. 2. Prior to the cleanup of samples, the cartridges mustt bewashed withh90:10hexane/acetone.This is accomplished by passing through at least 10 mL of thehexane/acetone solution through the each cartridge. NOTE: DO NOT ALLOW THE CARTRIDGES TO DRY AFTER THEY HAVEBEEN WASHED. If the cartridges go to dryness, add more solvent to wash it again. SOP: 1809 PAGE: 14 of 40 REV: 2.0 DATE: 01/23/06 ROUTINE ANALYSIS OF PESTICIDES IN SOIL/SEDIMENTSAMPLES BY GC/ECD (EPA/SW-846 Methods 3500B/3540C/3541/3600C/3640A/8000B/8081A) (EPA/SW-846 Methods 3600C/3620B/3660B -Optional) 3. After the cartridges in the manifold are washed, a rack containing labeled 25-mLconcentrator tubes is placed inside the manifold. Care must be taken to ensure that thesolvent line for each cartridge is placed inside of the appropriate concentrator tube as themanifold top is replaced. 4. After the concentrator tubes are in place, add approximately 1 mL of the mobile solution(90:10 hexane/acetone) to the florisil bed in the cartridge. Allow the solvent to pass intothe sorbent bed and immediately transfer 2 mL from each sample, blank and MS/MSDextract from Section 7.1, Step 16 to the top of the Florisil bed in the appropriate Florisilcartridge. 5. The pesticide extracts are then eluted through the cartridge with 18 mL of 90:10hexane/acetone and collected in 25-mL concentrator tubes held in the rack inside themanifold. NOTE: Be sure to add the 18 mL of mobile solution immediately after the 2-mL extract crosses the Florisil bed. 6. Transfer the concentrator tubes to the TurboVap and concentrate the extracts to a finalvolume of 2 mL using nitrogen blow down. 7.5 Tetrabutylammonium (TBA)-Sulfite Cleanup Elemental sulfur is encountered in many soil/sediment samples. The solubility of sulfur in theextraction and exchange solvents is very similar to the organochlorine pesticides; therefore, thesulfur is extracted along with the pesticides. If the GC is operated under normal conditions forpesticide analysis, the sulfur interference can completely mask the region from the solvent peakthrough aldrin. This cleanup is used to remove the sulfur interference. 1. Transfer 2 mL of extract from Section 7.1, Step 16 or Section 7.3, Step 5, to a 25-mLtest tube. 2. Add 2 mL of TBA-sulfite reagent and 2 mL of 2-propanol; cap and shake vigorouslywith a mechanical shaker such as Vortex for at least two minutes.If the sample iscolorless or if the initial color is unchanged, and if clear crystals (precipitated sodiumsulfite) are observed, sufficient sodium sulfite is present..If the precipitated sodiumsulfite disappears, add more TBA-sulfite reagent until a solid residue remains afterrepeated shaking. 3. Add 6 mL of deionized water and shake for at least two minutes. Allow the sample tostand for 5-10 minutes. 'Transfer the hexane layer (top) to two 1-mL injection vials.Analyze the extracts by GC/ECD. 7.6 SOP: 1809 REV: 2.0 DATE: 01/23/06 ROUTINE ANALYSIS OF PESTICIDES IN SOIL/SEDIMENTSAMPLES BY GC/ECD (EPA/SW-846 Methods 3600C/3620B/3660B -Optional) Copper cleanup requires that the copper powder be very reactive. 1. Transfer 2 mL of sample extract from Section 7.1 step 16 or Section 7.3, step 6 orSection 7.4 step 3, to a 4-mL screw-top vial. 2. Add approximately 0.5 to 2 g of copper powder (depends on the amount of sulfurpresent in the sample) to the vial. Vigorously mix the extract and copper powder for atleast 1 minute on a mechanical shaker such as Vortex. Allow the phases to separate. 3. Separate the extract from the copper by drawing off the extract with a disposable glasspipet into two 1-mL injection vials. 7.7 GC/ECD Conditions Sample analyses are performed using a Hewlett Packard (HP) 6890 GC/ECD, equipped with dualinjector, column, and electron capture detector capabilities. The HP 6890 conditions used for the pesticide analysis are listed below: Injector Temperature250°COven Temperature Program120°C hold for 1 minute (min)9C/min to 285°℃, 10 min at 285℃Detector Temperature300°CCarrier GasHeliumMake-up GasArgon/MethaneColumn Flow RateRTX-XLB 3.0 Milliliters/minute (mL/min);Rtx-CLPesticides 1 mL/minAmount Injected1 microliter (uL)Data SystemHP Chem Station The instrument conditions listed above are guidelines to be used for standards and sampleanalysis on a HP 6890 GC/ECD system. Any suitable conditions may be used as long as qualitycontrol criteria and peak separation is achieved. 7.8 Retention Time Windows Absolute retention times are used for compound identification. Retention time (RT) windows arecrucial for the identification of the target compounds. Absolute RT windows must be applied foreach analyte and surrogate on each column and instrument. Retention time windows are alsoestablished to compensate for shifts in absolute RTs as a result of instrument variability andsample loadings.The RT window must be carefully established to minimize the occurrence of SOP: 1809 PAGE: 16 of 40 REV: 2.0 DATE: 01/23/06 ROUTINE ANALYSIS OF PESTICIDES IN SOIL/SEDIMENTSAMPLES BY GC/ECD (EPA/SW-846 Methods 3500B/3540C/3541/3600C/3640A/8000B/8081A) (EPA/SW-846 Methods 3600C/3620B/3660B-Optional) false negatives or false positives. Due to advances in electronic pressure controls in modern GCs such as the HP6890, the RTsusually remain constant and may exhibit a negligible shift (nearly zero) over the traditional 72-hour period. A default standard value of ±0.030 minutes will be used for the two surrogates anda value of ±0.020 minutes will be used for the target analytes.These default values will beapplied unless the instrument and EPC unit cannot maintain constant retention times. If theinstrument cannot maintain reproducible RTs, the analyst must investigate the cause andimplement corrective action. Establish the absolute RT for each analyte and surrogate from thecalibration standard analyzed at the beginning of the analytical sequence. For samples runduring the same sequence as the initial calibration, use the RT of the 100 ug/L standard. NewRT windows must be calculated whenever a new column is installed. 7.8.1 Alternate Retention Time Window Determination 1. Make three injections of all pesticide standard mixtures over a 72-hour period. Theinjections may include initial calibration, continuing calibration and end ofsequence runs. All standard runs must be included in the RT window calculationunless a poor injection is observed. 2. Calculate the standard deviation (SD) ofthe absolute retention times for each targetcompounds including the surrogates and internal standards on both columns. Plusor minus three times the SD obtained during the 72-hour period is defined as thewidth of the RT window. 7.9 Standard and Sample Analysis 7.9.1 Pesticide Analysis (excluding toxaphene) The analytical sequence listed in Figure 1, Appendix B must be followed for singlecomponent and Figure 2, Appendix B must be followed for multi-componentcompounds. 1. Inject the working Resolution Check Standard and calculate the percentresolution between peaks. the depth of the valley between the peaks%Resolution=—x100peak height of the smaller peak being resolved The % resolution must be≥60.0% for all peaks to continue the analysis. SOP: 1809 PAGE: 17 of40 REV: 2.0 DATE:01/23/06 ROUTINE ANALYSIS OF PESTICIDES IN SOIL/SEDIMENTSAMPLES BY GC/ECD (EPA/SW-846 Methods 3500B/3540C/3541/3600C/3640A/8000B/8081A) (EPA/SW-846 Methods 3600C/3620B/3660B-Optional) 2. Inject the working PEM and calculate the percent breakdown (%BD) of 4,4'-DDT and endrin on the primary column by using either the peak height or peakarea using the following equations: Total Endrin Degradatin (endrinaldehyde and endrin kEndrin %BD=etone)-x100Total Endrin(endrin,endrin aldehydeand endrin ketone) Total DDT Degradatin (DDE and DDT)DDT%BD= -x100Total DDT(DDE,DDDand DDTendrin ketone) The %BD of 4,4'-DDT or endrin must not exceed 15.0%. If the requirement is not met,corrective action (injector maintenance and recalibration) must be taken before furtheranalyses can continue. If analytes are reported from both columns, the %BD must besupplied for both columns. 3. Prepare calibration standards as in Section 6.0.. Inject 1 uL each of the five singlecomponent calibration standards and tabulate the peak height or peak area for eachstandard concentration. Calculate the response factor (RF) for each compound at eachstandard concentration. The average RF and percent relative standard deviation(%RSD) must also be calculated for both columns using the equations below. where: A4x rea or Height of the characteristic ion of each target analyte Area of the characteristic ion of each internal standard assigned to targetanalytes Concentration of each internal standard (ng/mL) Concentration of each target analyte (ng/mL) SOP: 1809 REV: 2.0 ROUTINE ANALYSIS OF PESTICIDES IN SOIL/SEDIMENTSAMPLES BY GC/ECD (EPA/SW-846 Methods 3500B/3540C/3541/3600C/3640A/8000B/8081A) (EPA/SW-846 Methods 3600C/3620B/3660B -Optional) 4. Alternate External Standard Method Prepare calibration standards as in Section 6.0. Inject 1 pL each of the five singlecomponent calibration standards and tabulate the peak height or peak area for eachstandard concentration. Calculate the response factor (RF) for each compound at eachstandard concentration using the equation below. The average RF and %RSD must alsobe calculated for both columns using the equations above in Section 7.9.1 Step 3. RF=-Peak Area or Peak Height of AnalyteMass Injectedog The %RSD for each analyte must be ≤20% for the internal standard method andexternal standard method. If analytes are reported from both columns, the %RSD mustbe supplied for both columns. If the %RSD fails the critera for any of the compounds,the analyst may employ linear regression or a quadratic equation. The value of R’mustbe>0.98. NOTE:: An initial calibration curve must be run every six months at a minimum orsooner if the daily calibration check doesn’t meet the required percent difference (%D)as specified in Section 7.9.1, Step 6. 5 Inject 1 ppm each of Aroclor (Ar) 1016, Ar 1232, Ar 1242, Ar 1248, Ar 1254, Ar 1260,Ar 1268 and 2 ppm each of Ar 1221 and toxaphene as fingerprints. NOTE: The fingerprints are used for qualitative pattern matchingonly. Thefingerprints are not run with each initial calibration curve as long as the date of thefingerprints do not exceed one year or a new source of standards is received. 6. For every 12 hours of sample analysis, inject the 100 pg/L continuing calibrationstandard, which is mid-point of the curve. Calculate the %D of each compound in themixture using the following equation: T where: ARFin Initial Average Response FactorRFCALC =(Calculated Response Factor SOP: 1809 REV: 2.0 DATE:01/23/06 ROUTINE ANALYSIS OF PESTICIDES IN SOIL/SEDIMENTSAMPLES BY GC/ECD (EPA/SW-846 Methods 3500B/3540C/3541/3600C/3640A/8000B/8081A) (EPA/SW-846 Methods 3600C/3620B/3660B-Optional) The %D must be≤15.0% for all compounds. 7. Inject a group of sample extracts.It is recommended to inject the method blank andLCS first. All sample extracts must be analyzed within 12 hours of the injection of thePEM or the mid point standard. 8. At the end of the 12-hour period, inject a 100 pg/L pesticide standard as anothercalibration verification.. Calculate and tabulate the %D of all compounds. If allcompounds have a %D ≤15.0%, proceed to step 9. If not, necessary maintenance mustbe performed on the instrument prior to the analysis of any other sample extracts.Thesequence must be started from step 6. For additional criteria, refer to Section 9.0. 9. Inject another group of sample extracts. The extracts must be injected within 12 hoursof the injection of the 100 ug/L standard described in step 8.. The sequence will endwith the last injection of the 100 ug/L continuing calibration standard. The %D criteriamust be met prior to injecting any further sample extracts. 7.9.2 Toxaphene Analysis Identify the presence of toxaphene in the samples extracts using the toxaphenefingerprint standard run in Section 7.9.1, step 5. 1. Inject each of the five toxaphene calibration standards and choose 5 peaks in eachstandard to calculate RFs. If the toxaphene pattern changes from standard to standardor sample to sample, then the total area of all toxaphene peaks will be summed up inorder to calculate the average RF. The decision which method to use (5 peaks or totaltoxaphene peaks area) will be left to the discretion of the analyst. The RF and %RSDmust also be calculated for each toxaphene peak or total pattern area and surrogatesusing the equations in Sections 7.9.1 Step 3 and 7.9.1 Step 4. The average of 5 peaks or total toxaphene area %RSD and surrogates must beless than or equal to () 20.0%. NOTE:The initial curve must be run every six months at a minimum orsooner if the daily calibration check doesn’t meet the required percentdifference (%D) as specified in Section 7.9.1 Step 6. 2. Every 12 hours of sample analysis, inject the 2 ppm continuing calibrationcheck standard, which is the mid-point of the curve. Calculate and tabulate the%D of all 5 peaks or total toxaphene peaks area and the average the percentdifference must be ≤ 15% using the equation in Section 7.9.1 Step 6. SOP: 1809 PAGE: 20 of 40 REV: 2.0 DATE:01/23/06 ROUTINE ANALYSIS OF PESTICIDES IN SOIL/SEDIMENTSAMPLES BY GC/ECD (EPA/SW-846 Methods 3500B/3540C/3541/3600C/3640A/8000B/8081A) (EPA/SW-846 Methods 3600C/3620B/3660B-Optional) 3. Inject a group of sample extracts. It is recommended to inject a method blankand LCS first. All sample extracts must be analyzed within 12 hours of theinjection of the continuing calibration standard (step 2). Repeat steps 2 and 3, if necessary, until the %D requirement of the continuingcalibration check fails. End the sequence with the continuing calibration check standard. 7.9.3 PCB Analysis Identify the presence of PCBss inthe samplee eexxttracttss uusing the fingerprintchromatograms generated in Section 7.9.1, step 5. If PCBs are present,refer to SERASSOP #1801, Routine Analysis of PCBs in Water and Soil/Sediment by GC/ECD fordetailed analysis procedures. 7.10 Evaluation of Chromatograms All standard and sample chromatograms must be evaluated to determine if re-injection and/ordilution is necessary. 7.10.1 Standard/Sample Chromatograms The following requirements apply to all data generated for single component or multicomponent analytes: 4. The pesticide chromatograms must display the single component analytes andmulti component analytes present in each standard or sample at greater than(>)25% and less than (<) 100% of full scale. The chromatogram must beprinted in landscape mode with the time scale of the chromatogram fromapproximately 5 to 25 minutes (somewhere after the DCBP peak). If the timescale is modified, all chromatograms will be scaled the same for comparativepurposes. 5. If an extract is diluted, chromatograms must display single component or multicomponent pesticides between 10% and 100% of full scale. 6. If a chromatogram is re-plotted electronically to meet requirements, the scalingfactor used must be displayed on the chromatogram. 7. If a chromatogram show carryover from a previous injection, subsequent SOP: 1809 PAGE: 21 of 40 REV: 2.0 DATE:01/23/06 ROUTINE ANALYSIS OF PESTICIDES IN SOIL/SEDIMENTSAMPLES BY GC/ECD (EPA/SW-846 Methods 3500B/3540C/3541/3600C/3640A/8000B/8081A) (EPA/SW-846 Methods 3600C/3620B/3660B-Optional) sample extract(s) must be re-analyzed, preferably immediately. 8. The retention time of each single component analyte must fall within the RTwindows on both columns as determined in Section 7.8. Ifthe RT window hasshifted in the thousandth place (>0.020 but <0.030 for target analytes and>0.030 but <0.040 for surrogates), professional judgement may be used todetermine the acceptability of the data. If the RT is shifted by more than ±0.030 minutes for the target analytes and +0.040 minutes for the surrogates, theanalytical sequence (acquisition) must be interrupted for corrective action.After corrective action, acquisition of data can be resumed only after anacceptable PEM and 100 ppb pesticide standard is obtained. No retention timewindow is required for toxaphene analysis since the identification of toxapheneis done by pattern recognition. 9. If it is determined that the matrix may be causing a RT shift, the MS/MSD inconjunction with the original sample chosen for spiking may be used to assessmatrix effects. 10. If a sample chromatogram has interfering peaks, a high baseline, or off-scalepeaks, the sample extract must be re-analyzed using a dilution or furthercleanup techniques. In some instances, re-extraction may be performed.Samples that do not meet acceptance criteria after one re-extraction andcleanup must be reported in the case narrative and do not require furtheranalysis. 11. If there are two peaks within a RT window, the data will be reported from theother column with one peak within the window. 12. If manual integrations have been performed, refer to SERAS SOP #1001,Chromatographic Peak Integration Procedures for appropriate documentationprocedures. 7.10.2 Pesticide Identification The identification of single component pesticides is based primarily on RT data.Theretention time of the apex of the peak can only be verified from an on-scalechromatogram.The identification of toxaphene 1sprimarily based on patternrecognition, which can only be verified from an on-scale chromatogram. Secondcolumn confirmation is optional for toxaphene analysis. 1. Single component analytes are identified when peaks are observed in the RTwindows for the compound on both GC columns.The identification of multi SOP: 1809 PAGE: 22 of 40 REV: 2.0 DATE: 01/23/06 ROUTINE ANALYSIS OF PESTICIDES IN SOIL/SEDIMENTSAMPLES BY GC/ECD (EPA/SW-846 Methods 3500B/3540C/3541/3600C/3640A/8000B/8081A) (EPA/SW-846 Methods 3600C/3620B/3660B -Optional) component is primarily based on pattern recognition, which can only beverified from an on-scale chromatogram. Second column confirmation isoptional for toxaphene analysis. 2. If a peak is just outside any target compound’s RT window, examine theretention time of the closest surrogate, internal standards, matrix spikecompounds, and the closest calibration check. Use retention times to evaluate apossible RT shift. Similar RT shifts of target compounds can be expected inSome cases. 3. If a sample contains interfering peaks or a high baseline, further cleanup maybe necessary. Compound identification on this type of sample may be difficult.Information such as surrogate RT, peak ratio on both GC columns,and samplehistory must be evaluated for identification purposes. 4. If quantifying on both columns and the RPD >40% for a particular analyte,report the highest concentration and flag as estimated (J) for that analyte only.Calculate the % RPD using the equation in Section 8.4. 7.11 Sample Dilution Target compound concentrations must not exceed the upper limit of the initial calibration range.If analytes are detected in the extract at a level greater than the highest calibration standard, theextract must be diluted (to a maximum of 1:100,000) or until the analyte response is within thelinear range established during calibration. Guidance in performing dilutions and exceptions tothis requirement are given below. 1. If the analyst has reason to believe that diluting the final extracts will be necessary basedon historical data or visual observation of the extracts, an undiluted run may not berequired. However, if no peaks are detected above 25% of full scale on the dilutedsample, analysis of a more concentrated sample extract or the undiluted sample extractis required. 2. Ifthe response is still above the highest calibration point after the dilution of 1:100,000,the analyst should contact the Organic Group Leader immediately for furtherinstruction. 3. The results of the original analysis are used to determine the approximate dilution factorrequired to bring the largest analyte peak within the initial calibration range. 4. The dilution factor chosen should keep the response of the largest peak for a targetcompound in the initial calibration range of the instrument. SOP: 1809 REV: 2.0 DATE: 01/23/06 ROUTINE ANALYSIS OF PESTICIDES IN SOIL/SEDIMENTSAMPLES BY GC/ECD (EPA/SW-846 Methods 3500B/3540C/3541/3600C/3640A/8000B/8081A) (EPA/SW-846 Methods 3600C/3620B/3660B -Optional) 5. Submit data for any reportable analyses. 6. All chromatograms for the dilution analyses must meet the requirements described inSection 7.10. 8.0 CALCULATIONS Quantitation of target compounds and surrogates can be performed on any column that passed all thequality control (QC) criteria specified in this SOP. In order to be quantitated, the detector response (peakarea or peak height) of all the analytes must lie within the calibration range. 8.1 Reporting Limit for Soil where: = Dilution factor (ifany) CsTD= Concentration of the lowest standard in the calibration range(ug/mL)=Volume of the extract (mL)WS = Weight of soil/sediment extracted, kilograms (kg) = Decimal percent solids 8.2 Sample Concentration for Soil 8.2.1 Internal Standard Method Identified target analytes will be quantitated by the internal standard method.TTheinternal standard used must be the one nearest the retention time to that of the givenanalyte listed in Table 2, Appendix A. Use the following equation to calculate the concentration of the identified analytes usingthe average relative response factor (RRF) obtained from the initial calibration curve. where: SOP: 1809 REV: 2.0 DATE:01/23/06 ROUTINE ANALYSIS OF PESTICIDES IN SOIL/SEDIMENTSAMPLES BY GC/ECD (EPA/SW-846 Methods 3500B/3540C/3541/3600C/3640A/8000B/8081A) (EPA/SW-846 Methods3600C/3620B/3660B -Optional) A= Peak Area or Peak Height of each target analytehA =Amount of each internal standard injected (ng) = Volume of the concentrated extract (mL) =Dilution factor = Peak Area or Peak Height of each internal standard RRFavg= Average Relative response factor W= Weight of soil/sediment extracted (kg)S =Decimal percent solid = Injection volume (usually 1 pL) 8.2.2 Alternate External Standard Method Unusual sample matrices which may interfere with the internal standards,and/orunusual circumstances encountered during sample analysis may warrant the use of theexternal standard method with the discretion of the Organic Group Leader. where: =Peak area or Peak height for the compound to be measured =Volume of the concentrated extract (mL) =Dilution factor (if any) RRFavgg=Average response factor Ws = Weight of soil/sediment extracted (kg) =Volume of extract injected (uL) =Decimal percent solids For the quantitation of PCB concentrations, refer to SERAS SOP #1801, RoutineAnalysis ofPCBs in Water and Soil/Sediment by GC/ECD. NOTE: If any analytes are detected below the reporting limit at >25% of the reportinglimit, report the concentration and flag as estimated (J) otherwise reported asundetected. 8.3 Surrogate Spike Recoveries where: SOP: 1809 REV: 2.0 DATE:01/23/06 ROUTINE ANALYSIS OF PESTICIDES IN SOIL/SEDIMENTSAMPLES BY GC/ECD (EPA/SW-846 Methods 3500B/3540C/3541/3600C/3640A/8000B/8081A) (EPA/SW-846 Methods 3600C/3620B/3660B-Optional) = quantity determined by analysis一 quantity added to sample 8.4 Matrix Spike Recoveries The percent recoveries and the relative percent difference (RPD) between the recoveries of eachof the six pesticide compounds are calculated and reported using the following equation: where: SSR spike sample result sample result — spike added where: RPD = relative percent difference MSR = matrix spike recovery MSDR= matrix spike duplicate recovery The vertical bars in the formula above indicate the absolute value of the difference; hence, RPD isalways expressed as a positive value. 8.5 Laboratory Control Sample Recoveries The recoveries of each of the compounds in the LCS solution will be calculated using thefollowing equation: where: LCSR = Concentration of target analyte in LCS B Concentration of target analyte in blank SA Concentration of spike added SOP: 1809 REV: 2.0 ROUTINE ANALYSIS OF PESTICIDES IN SOIL/SEDIMENTSAMPLES BY GC/ECD (EPA/SW-846 Methods 3500B/3540C/3541/3600C/3640A/8000B/8081A) (EPA/SW-846 Methods 3600C/3620B/3660B-Optional) 9.0 QUALITY ASSURANCE/ QUALITY CONTROL 9.1 Holding Time Extraction of soil/sediment samples must be completed within 7 days of sampling, and analysiscompleted within 40 days of sample extraction. 9.2 Identification of Target Compounds Each target compound identified on the primary column within the RT window ofa singlecomponent pesticide must be confirmed within the compound’s RT window on the secondarycolumn in order to be reported. The identification of multi component toxaphene is primarilybased on pattern recognition and only reported from the primary column.Second columnconfirmation is optional for toxaphene analysis. 9.3 GC Column Performance The resolution check demonstrates that the GC column is capable of chromatographicallyresolving the pesticide target compounds. The Resolution Check is not required for the analysisof toxaphene only. 2. The Resolution Check mixture must be analyzed at the beginning of every initialcalibration sequence, on each GC column for the instrument used for pesticide analysis. 3. The percent resolution must be greater than or equal to 60% prior to the analysis ofstandards, samples or blanks on both columns. 9.4 Initial Calibration for Target Compounds and Surrogates Prior to the analysis of any sample, method blank, or MS/MSD, the GC/ECD system must beinitially calibrated at a minimum of five concentrations to determine the linearity range for alltarget compounds and surrogates.If reporting data from only one column, the RSDs will bereported from only that column. If reporting data from both columns, all correspondingcalibrations will be required for both columns. 1. The concentration of all calibration standards that are specified in Section 6.0 must beused. 2. The standards are to be analyzed according to the procedures given in Section 7.9 usingthe GC operating conditions in Section 7.7. SOP: 1809 PAGE: 27 of 40 REV: 2.0 DATE:01/23/06 ROUTINE ANALYSIS OF PESTICIDES IN SOIL/SEDIMENTSAMPLES BY GC/ECD (EPA/SW-846 Methods 3500B/3540C/3541/3600C/3640A/8000B/8081A) (EPA/SW-846 Methods 3600C/3620B/3660B -Optional) 3. The response factors are determined according to the procedure in Section 7.9. 4. The calibration is evaluated on the basis of the extent of endrin and 4,4'-DDTbreakdown, as described in Section 7.9.2. The breakdown ofeither DDT or endrin mustnot exceed 15.0%. 5. The initial calibration is also evaluated on the basis of the stability of the responsefactors of each target compound and surrogate. The %RSD of each target compoundmust not exceed 20.0%.).If the %RSD fails the critera for any of the compounds, theanalyst could employed linear regression or quadratic equations. The value of R²mustbe >0.98. 9.5 Continuing Calibration for Target Compounds and Surrogates Once the GC/ECD system has been calibrated, the calibration must be verified each 12-hour timeperiod during which samples are analyzed. If reporting data from only one column, the %D willbe calculated from that column only.V.If reporting data from both columns, the %Ds will berequired for both columns. 1. The continuing calibration is evaluated on the basis of the stability of the instrumentresponse to the target compounds present in the PEM and the mid-point standard. 2. If a specific analyte in the standard analyzed after a group of samples exhibits a response>15.0 % and the analyte was not detected in any of the samples, the extracts do not haveto be re-analyzed. 3. If the % D exceeds 15.0% for a specific analyte and the analyte is present in the sampleextract, re-injection is required to ensure an accurate concentration. 4. If the % D for the end of sequence (EOS) standard exceeds 15.0% for a specific analyteand the analyte is present in the sample, the samples after the last good standard must bere-analyzed in another sequence.If the EOS standard still does not meet acceptancecriteria after re-analysis, document the result in the case narrative and further analysis isnot required. 9.6 Retention Time Windows 1. The identification of single component pesticide by GC is based primarily on retentiontime data. Therefore, the determination of retention time windows is crucial for theproduction of valid data (Section 7.8). No retention time windows are required formulti-component compounds. Refer to SERAS SOP #1801, Routine Analysis of PCBsin Water and Soil/Sediment by GC/ECD. SOP: 1809 REV: 2.0 DATE: 01/23/06 ROUTINE ANALYSIS OF PESTICIDES IN SOIL/SEDIMENTSAMPLES BY GC/ECD (EPA/SW-846 Methods 3500B/3540C/3541/3600C/3640A/8000B/8081A) (EPA/SW-846 Methods 3600C/3620B/3660B -Optional) 2. The identification of all target compounds analyzed by this SOP is based on the use ofabsolute retention time. 3. The retention time window for each target compound is determined in accordance withSection 7.8. 4. The retention time shifts of the internal standard may be used to evaluate the stability ofthe GC system during the analysis of standards only. 5. Retention time windows must be established on both columns and submitted with thedata package to support the pesticide identifications reported. 9.7 Analytical Sequence The standards and samples analyzed by this SOP must be analyzed in a sequence outlined inFigure 1, Appendix B..This sequence includes requirements that apply to the initial andcontinuing calibrations, as well as the analysis of samples. 9.8 Method Blank and Laboratory Control Sample A method blank and LCS is a known weight of a clean reference matrix (pure sand or bakedsodium sulfate) that is carried through the entire analytical procedure. The weight used for themethod blank and LCS must be approximately equal to the weight of the samples associated withthe blank. The purpose of the method blank and LCS are to determine if there are anycontaminants associated and the proficiency of the process and analysis of samples. 1. A method blank and LCS must be prepared for each group of up to 20 samples extractedat the same time or per batch and analyzed on each GC/ECD system used to analyzesamples. 2. A method blank must not contain any of the compounds listed in Table 1, Appendix Aat concentrations greater than or equal to () the reporting limit. 3. Samples associated with an unacceptable method blank re-ext. ass(racted and re-analyzed ifsufficient sample mass is available and the holding time has not been exceeded.Otherwise, it will be documented in the case narrative. If contaminants are observed inthe method blank but not in the samples, note it in the case narrative and sample re-analysis is not required. 4. When sample extracts are subjected to cleanup procedures, the associated method blankmust also be subjected to the sample cleanup procedure. Method blank must be SOP: 1809 PAGE: 29 of 40 REV: 2.0 DATE: 01/23/06 ROUTINE ANALYSIS OF PESTICIDES IN SOIL/SEDIMENTSAMPLES BY GC/ECD (EPA/SW-846 Methods 3500B/3540C/3541/3600C/3640A/8000B/8081A) (EPA/SW-846 Methods 3600C/3620B/3660B-Optional) analyzed on all instruments used for sample analysis, this does not include the dilutionrun. 5. Method blank results must not be subtracted from any associated samples. 6. Use 70 to 130% for LCS recoveries until ranges are established. LCS % recovery lessthan 70% must be reported to the Organic Group Leader. 9.9 Surrogate Recoveries 1. Surrogates are added to each sample, blank, LCS, MS, and MSD prior to extraction atthe concentrations described in Sections 6.0 and 7.1. 2. The surrogate spike recoveries are calculated according to the procedures in Section 8.3. 3. The quality control limit for both surrogate recoveries is 30 -150%.).These limits areonly advisory, and no further action is required if the limits are exceeded. However,frequent failures to meet the limits for surrogate recovery warrant investigation by thelaboratory. 9.10 Internal Standards 1. Internal standards must be added to all standards and samples including the lab blanks,LCSs and MS/MSDs to achieve a final concentration of 100 pg/L. 2. The peak height (or area) of the internal standards in each sample must be monitoredby the analyst and to assure the height (or area) falls between 50% and 150% of thecorresponding internal standard in the daily calibration check.If any the internalstandards do not meet the criteria (50% to 150%), then it will be flagged with (*). Note: Only the internal standards used to calculate the target compounds will be monitored. 3. If one or more internal standard areas do not meet criteria, the GC system must beinspected for malfunctions and corrections made as appropriate. When corrections aremade, re-analysis of all affected samples is required. If re-analysis is not feasible due tomatrix interference (i.e., coeluting with IS peak) on both columns, the analyst maychoose to dilute the sample to remove the interference instead of re-analyzing. 4. If after re-analysis, the areas for all internal standards meet criteria (between 50% and150%), then the problem with the first analysis is considered to have been within thecontrol of the laboratory. Therefore, only data from the analysis with the ISs withinlimits are required to be submitted. If re-analysis confirms matrix effects, submit both SOP: 1809 PAGE: 30 of40 REV: 2.0 DATE:01/23/06 ROUTINE ANALYSIS OF PESTICIDES IN SOIL/SEDIMENTSAMPLES BY GC/ECD (EPA/SW-846 Methods 3500B/3540C/3541/3600C/3640A/8000B/8081A) (EPA/SW-846 Methods3600C/3620B/3660B -Optional) sets of data but report the initial run. 9.11 Matrix Spike and Matrix Spike Duplicate Analysis The purpose of spiking target compounds into two portions of a sample is to evaluate the effectsof the sample matrix on the methods used in this SOP. 1. The MS/MSD must be prepared with every 10 samples per matrix or per project,whichever is more frequent. 2. The matrix spiking solution specified in Section 6.0 must be used and result in theconcentration specified in Section 7.1. 3. The recoveries of the MS compounds are calculated according to the procedures inSection 8.4.. The %RPD for each spiked analyte are calculated between the results of theMS and the MSD according to the procedures in Section 8.4. 4. The client-specified MS recovery limits are taken from the CLP Statement of Work(revision 5/99) and are as follows: Note If the laboratory fails to meet the recovery QC limits and the RPD limits on aroutine basis, the: Organic Group Leader must investigate the cause and take correctiveaction. State in case narrative if recoveries are outside criteria. If more than half of the spikedcompounds are out, the MS/MSD should be reanalyzed. A matrix effect is indicated ifthe LCS data are within limits but the MS/MSD are not. A similar pattern must beobserved for both the MS andMSD. If the lab fails to meet the QC recovery limits and/or the RPD on a routine basis, theOrganics Group Leader must investigate the cause and take corrective action. TheMS/MSD must be prepared at the same dilution as the least diluted analysis from whichsample results will be reported. SOP: 1809 PAGE: 31 of 40 REV: 2.0 DATE: 01/23/06 ROUTINE ANALYSIS OF PESTICIDES IN SOIL/SEDIMENTSAMPLES BY GC/ECD (EPA/SW-846 Methods 3500B/3540C/3541/3600C/3640A/8000B/8081A) (EPA/SW-846 Methods3600C/3620B/3660B -Optional) 5. The sample and MS/MSD must be analyzed and reported from at the same dilutionfactor. 6. A MS/MSD must be analyzed every 10 samples or per project. The MS/MSD must beassociated with a method blank that meets the criteria in section 9.8, a calibration insections 9.4 and 9.5. The MS/MSDs should be run on the same 12-hour shift as thesample. 9.12 Initial Demonstration of Capability Initial proficiency in pesticide and toxaphene analysis must be demonstrated by each analystinitially and each time significant changes are made in th+;11..e procedure or for instrumentation.Each analyst will generate precision and accuracy data using a reference standard other than thesource used for calibration. Four replicate of a well-mixed reference standard is analyzed usingthe procedures outlined in this SOP. Calculate the average mean in ug/kg and the standarddeviation (S)in ug/kg. The Quality Assurance Officer (QAO) will tabulate the results from all ofthe analysts per matrix per parameter, and calculate control limits. 9.13 Dilution Analysis If the concentration of any sample extract exceeds the initial calibration range, that sampleextract must be diluted and re-analyzed as described in Section 7.11. If there are no peaksdetected above 25% of the full scale in the dilution analysis, a lower dilution of the sampleextract must be analyzed. 9.14 Reporting Limit The lowest concentration of the calibration standard that is analyzed during the initial calibrationdetermines the method reporting limit based on the initial weight of the sample, final volume ofextract obtained from the extraction, and the percent total solids. 9.15 Method Detection Limit Studies Method detection limit (MDL) studies will be run on an annual basis for the soil matrix to verifythe minimum concentration that can be measured and reported with 99% confidence. Aminimum of seven replicates will be used for the study (EPA 1984). 9.16 Nonconformance Memo A nonconformance memo will be generated any time an employee notices a deficiency suspectedof being a nonconformance. This nonconformance memo will be forwarded to the QAO forverification of corrective action. SOP: 1809 PAGE: 32 of 40 REV: 2.0 DATE:01/23/06 ROUTINE ANALYSIS OF PESTICIDES IN SOIL/SEDIMENTSAMPLES BY GC/ECD (EPA/SW-846 Methods 3500B/3540C/3541/3600C/3640A/8000B/8081A) (EPA/SW-846 Methods 3600C/3620B/3660B-Optional) 10.0 DATA VALIDATION Data will be assessed in accordance with the guidelines set forth in the most recent version of the SERASdata validation SOPs. However, data is considered satisfactory for submission purposes when ALL therequirements mentioned below are met. l. Al samples must be analyzed as part of a valid analytical sequence, i.e., an acceptable initialcalibration, and continuing calibration check at the required frequency. 2. All the QC requirements described in Section 9.0 must be met at all times. Any deviations oranomalous conditions should be discussed with the Organic Group Leader. 11.0 HEALTHAND SAFETY When working with potentially hazardous materials, refer to EPA, Occupational Safety and HealthAdministration (OSHA) and corporate health and safety practices. More specifically, refer to SERASSOP #3013, SERAS Laboratory Safety Program and SERAS SOP #1501, Hazardous Waste Management. 12.0 REFERENCES National Environmental Laboratory Accreditation Committee (NELAC), Quality Systems, currentapproved version. United States Environmental Protection Agency, Office of Solid Waste and Emergency Response.1996.Test Methods for Evaluating Solid Waste, SW-846, 3" ed., Method 3500B. United States Environmental Protection Agency, Office of Solid Waste and Emergency Response. 1996.Test Methods for Evaluating Solid Waste, SW-846, 3 ed., Method 3600C. United States Environmental Protection Agency, Office of Solid Waste and Emergency Response. 1996.Test Methods for Evaluating Solid Waste, SW-846, 3"ded., Method 3620B. United States Environmental Protection Agency, Office of Solid Waste and Emergency Response. 1994.Test Methods for Evaluating Solid Waste, SW-846,3" ed., Method 3640A. United States Environmental Protection Agency, Office of Solid Waste and Emergency Response. 1996.Test Methods for Evaluating Solid Waste, SW-846,3"d ed.,Method 3660B. United States Environmental Protection Agency, Office of Solid Waste and Emergency Response. 1996.Test Methods for Evaluating Solid Waste, SW-846, 3 ed., Method 8000B. SOP: 1809 PAGE: 33 of 40 REV: 2.0 DATE: 01/23/06 ROUTINE ANALYSIS OF PESTICIDES IN SOIL/SEDIMENTSAMPLES BY GC/ECD (EPA/SW-846 Methods3500B/3540C/3541/3600C/3640A/8000B/8081A) (EPA/SW-846 Methods 3600C/3620B/3660B-Optional) United States Environmental Protection Agency, Office of Solid Waste and Emergency Response. 1996.Test Methods for Evaluating Solid Waste, SW-846, 3 ed., Method 8081A. United States Environmental Protection Agency, Contract Laboratory Program (CLP). 1999. Statement ofWork for Organic Analysis, OLM04.2. United States Environmental Protection Agency. 1984. Federal Register, 40 Code of Federal Regulations(CFR) Part 136, Appendix B, Definition and Procedure of the Determination of the Method DetectionLimit -Revision 1.11, October 26, 1984. 13.0 APPENDICES A-Table B-Figure SOP: 1809 PAGE: 34 of 40 REV: 2.0 DATE:01/23/06 ROUTINE ANALYSIS OF PESTICIDES IN SOIL/SEDIMENTSAMPLES BY GC/ECD (EPA/SW-846 Methods 3500B/3540C/3541/3600C/3640A/8000B/8081A) (EPA/SW-846 Methods 3600C/3620B/3660B-Optional) APPENDIX A Tables SOP #1809 January 2006 SOP: 1809 REV: 2.0 DATE:01/23/06 ROUTINE ANALYSIS OF PESTICIDES IN SOIL/SEDIMENTSAMPLES BY GC/ECD TABLE 1. Target Compound List and Typical Reporting Limits for Soil COMPOUND RL"(ug/kg) a-BHC 3.33 Y-BHC 3.33 B-BHC 3.33 Heptachlor 3.33 8-BHC 3.33 Aldrin 3.33 Heptachlor epoxide 3.33 a-Chlordane 3.33 y-Chlordane 3.33 Endosulfan I 3.33 4,4'-DDE 3.33 Dieldrin 3.33 Endrin 3.33 4,4'-DDD 3.33 Endosulfan II 3.33 4,4'-DDT 3.33 Endrin aldehyde 3.33 Endosulfan sulfate 3.33 Methoxychlor 3.33 Endrin ketone 3.33 Toxaphene 83.3 (1) RL denotes Reporting Limits on a wet weight basis SOP: 1809 REV: 2.0 DATE: 01/23/06 ROUTINE ANALYSIS OF PESTICIDES IN SOIL/SEDIMENTSAMPLES BY GC/ECD (EPA/SW-846 Methods 3500B/3540C/3541/3600C/3640A/8000B/8081A) (EPA/SW-846 Methods 3600C/3620B/3660B-Optional) TABLE 2. Target Compound List and Internal Standards 4,4'-Dibromooctafluorobiphenyl (IS) TCMX a-BHC y-BHC β-BHC 8-BHC Heptachlor Aldrin Toxaphene 4,4'-Dibromobiphenyl (IS) Heptachlor epoxide a-Chlordane y-Chlordane Endosulfan I 4,4'-DDE Dieldrin Endrin 4,4'-DDD 3,3',4,4'-Tetrabromobiphenyl (IS) Endosulfan II Endrin aldehyde 4,4'-DDT Endosulfan sulfate Methoxychlor Endrin ketone DCBP SOP: 1809 PAGE: 37 of 40 REV: 2.0 DATE:01/23/06 ROUTINE ANALYSIS OF PESTICIDES IN SOIL/SEDIMENTSAMPLES BY GC/ECD (EPA/SW-846 Methods 3500B/3540C/3541/3600C/3640A/8000B/8081A) (EPA/SW-846 Methods 3600C/3620B/3660B-Optional) APPENDIX B Figures SOP#1809 January 2006 SOP: 1809 REV: 2.0 ROUTINE ANALYSIS OF PESTICIDES IN SOIL/SEDIMENTSAMPLES BY GC/ECD (EPA/SW-846 Methods 3600C/3620B/3660B-Optional) FIGURE 1. Pesticide Analytical Sequence Time Injection # Material Injected Resolution Check 2 Performance Evaluation Mix (PEM) 3-7 Initial Calibration (5-point) 8-16 Toxaphene and PCB Fingerprints 0 hr. 17 PEM or 100 ppb Pesticide Standard 18 100ppb Pesticide Standard or PEM 19 1t Sample Subsequent Samples 12 hr. Continuing Calibration Check Standard Samples another 12 hr. Continuing Calibration Check Standard Samples another 12 hr. Continuing Calibration Check Standard Samples etc. last Continuing Calibration Check Standard NOTE: All subsequent 12-hour periods are timed from the injection of the PEM or the mid-point calibrationstandard. The analytical sequence must end with a continuing calibration check standard. SOP: 1809 REV: 2.0 ROUTINE ANALYSIS OF PESTICIDES IN SOIL/SEDIMENTSAMPLES BY GC/ECD (EPA/SW-846 Methods 3600C/3620B/3660B-Optional) FIGURE 2. Analytical Sequence for Toxaphene Analysis Time Injection # Material Injected 0 hr. 1-5 Toxaphene Calibration (5-point) 12 hr. n 1st Sample Sequence 2 ppm Toxaphene Continuing Calibration Standard and/or End of n+1 1st Sample another 12 hr. o Sequence 2 ppm Toxaphene Continuing Calibration Standard and/or End of Sequence Samples another 12 hr. 2 ppm Toxaphene Continuing Calibration Standard and/or End of Sequence another 12 hr. Samples 2 ppm Toxaphene Continuing Calibration Standard and/or End of Sequence Samples etc. NOTE: All subsequent 12-hour periods are timed from the injection of the mid-point calibration standard. Theanalytical sequence must end with a continuing calibration check standard (2 ppm toxaphene). The mid-pointcalibration standard from the initial calibration curve can be used as the daily check. SOP: 1809 PAGE: 40 of 40 REV: 2.0 DATE: 01/23/06 ROUTINE ANALYSIS OF PESTICIDES IN SOIL/SEDIMENT SAMPLES BY GC/ECD (EPA/SW-846 Methods 3500B/3540C/3541/3600C/3640A/8000B/8081A) (EPA/SW-846 Methods 3600C/3620B/3660B -Optional) APPENDIX C Soxthernm Operating Conditions SOP #1809 January 2006 Soxtherm Extraction Operating Conditions for Pesticide/PCBs and Toxaphene SOP: 1809 PAGE: 41 of 40 REV: 2.0 DATE:01/23/06 ROUTINE ANALYSIS OF PESTICIDES IN SOIL/SEDIMENTSAMPLES BY GC/ECD 溶剂调节冷浸提回流 浓缩 快速提取 ExtractionTemp. SolventVolume SolventType HotExtractionTime EvaporationA Rinsing Evaporation BInterval EvaporationC 160 140 mL hex/ace (1:1) 5x Interval TimeElapsed 50 min 25 min 30 min 15 min VolumeExpected 140 mL 65 mL 50 mL 50 mL 50 mL TotalElapsedTime 55 min 80 min 110 min 110 min 120 min 溶剂使用了140ml,传统需要300ml,节省了160ml 总共2小时 140ml通过溶剂调整和浓缩到50ml SUPERSEDES: SOP # Revision .; U.S. EPA Contract EP-W- Copper Cleanup This standard operating procedure (SOP) is applicable to the determination of organochlorine pesticides with the possible presence of polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) or toxaphene in soil/sediment matrices using a gas chromatograph (GC) with a narrow-bore fused silica column and an electron capture detector (ECD). This SOP is based on Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) MethodSW846/3500B/3540C/3541/8000B/8081A and those requirements set forth in the latest approved version of the National Environmental Laboratory Accreditation Committee (NELAC) Quality Systems section. Gel permeation chromatography [GPC] cleanup is required and is based on EPA/SW-846 Methods 3600C/3640A. Extracts may be subjected to optional cleanup procedures (florisil, tetrabutylammonium [TBA] sulfite or activated copper powder) based on EPA/SW-846 Methods 3600C/3620B/3660B. The compounds of interest and typical reporting limits (RLs) in soil/sediment matrices are found in Table 1, Appendix A.
确定






































还剩39页未读,是否继续阅读?
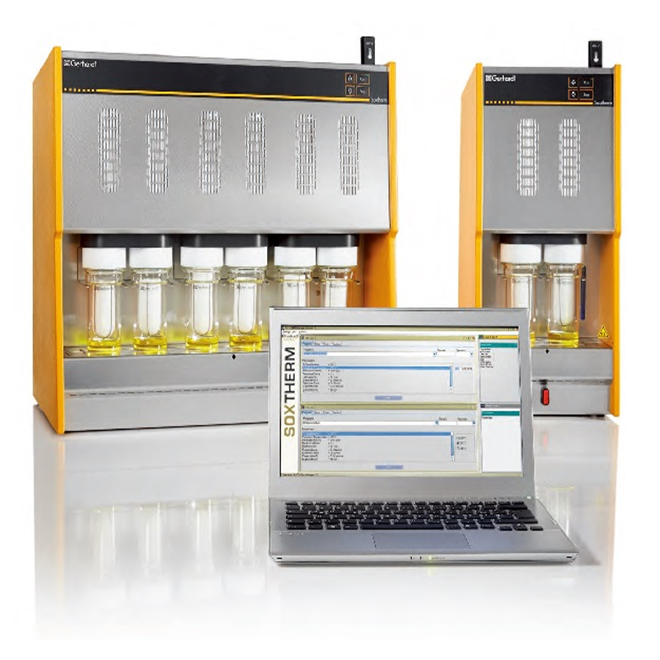
中国格哈特为您提供《土壤、沉积物中多氯联苯(PCBs)和毒杀芬检测方案(快速溶剂萃取)》,该方案主要用于土壤中有机污染物检测,参考标准--,《土壤、沉积物中多氯联苯(PCBs)和毒杀芬检测方案(快速溶剂萃取)》用到的仪器有格哈特全自动快速溶剂萃取仪Sox416、德国移液器MM
相关方案
更多
该厂商其他方案
更多











