
方案详情
文
In recent years, the gemstone market has been flooded with stones of questionable origin. Frequently, even thorough analysis by a qualified jeweler cannot unequivocally reveal whether
方案详情

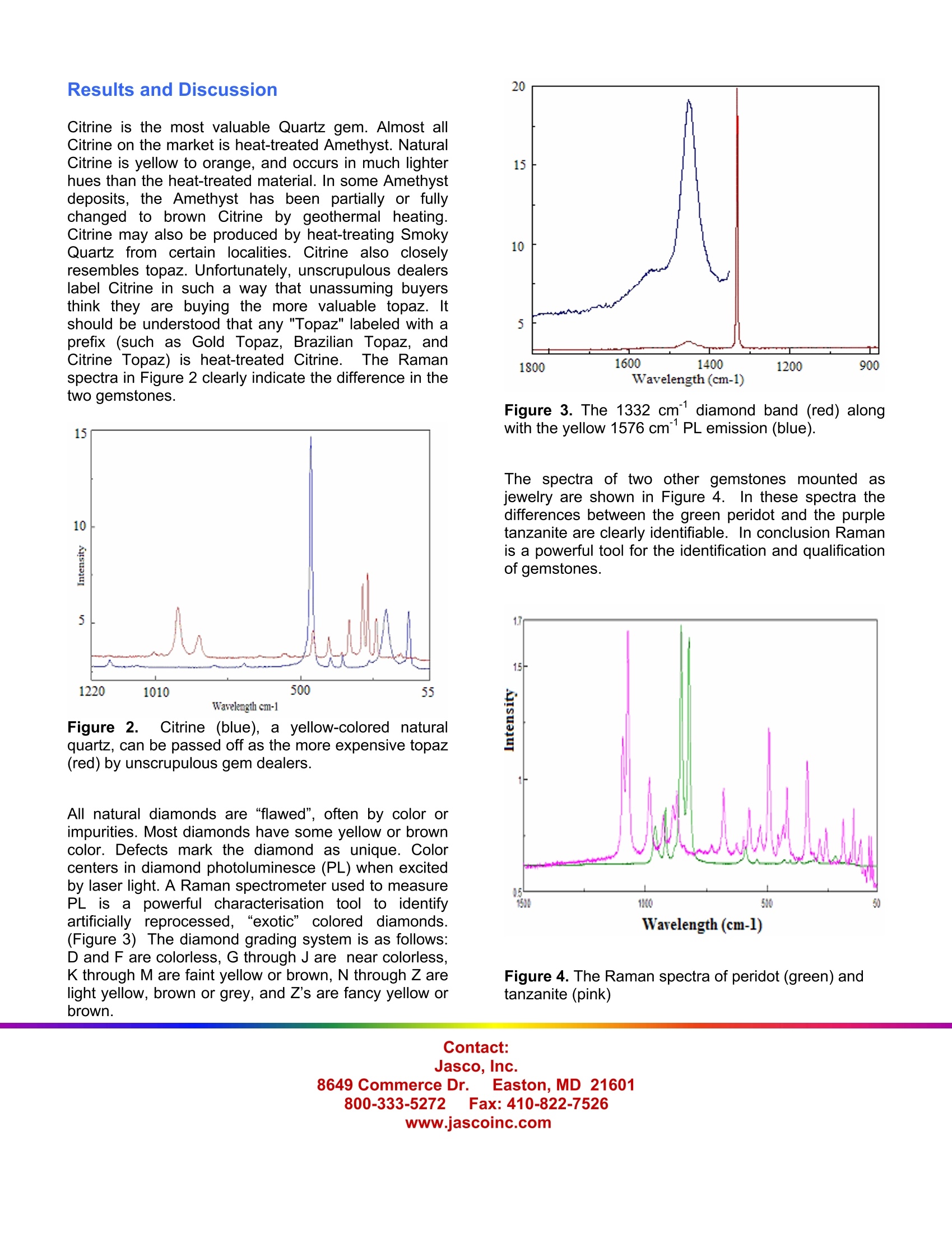
Contact:Jasco, Inc.8649 Commerce Dr. Easton, MD 21601800-333-52722 Fax:410-822-7526www.jascoinc.com RM APPLICATION NOTE 01-03Gemstone Identification UsingRaman Spectroscopy In recent years, the gemstone market has beenfloodedwith stones fiCquestionable: origin.Frequently, even thorough analysis by a qualifiedjeweler cannot unequivocally reveal whether agemstone is genuine or fake. In the worst case,even sophisticated analytical methods struggle todifferentiate modified diamonds, causingconsiderable concern to the internationalgemstone trade. Raman micro-spectroscopy is anideal method for the examination of marketablegemstones. The lack of sample preparation and thenon-destructive nature of Raman analysis make itideal for the analysis of even high-value gems.Plus, the micro-Raman study of a stone provides aunique record for identification purposes. We willdiscuss the variety of Raman spectra that can beobtained from different families of gemstones,comparing and contrasting spectra from genuineand artificial materials. Introduction Gemstones and semi-precious stonesirhave beenmodified for centuries to make them more colorful,more eye-catching, and easier to work with. One suchtechnique is heat treating (the most common) toenhance, clarify or create color in a stone. Amethyst isheated for citrine. Zircon is heated to clarify the stoneto clear white. Sapphires are heated to get amazingpinks and blues. Rubies lose a purplish tint while iolitemay be turned a deep blue. Heat treating can also beused to enhance the ‘color change’of gems such astanzanite. Dying of stones is also a very commonpractice. Agate is dyed to get pinks, purples, orangeand blues. Chalcedony is also dyed; black chalcedonysold as onyx. Irradiation is another common treatment.Topaz is currently the most commonly irradiatedgemstone (to get various shades and tones of blue).This is also how one obtains fabulously coloreddiamonds. In fact, diamond was the first gemstone tobe color treated by radiation. (Figure 1) Anothergemstone modification is stabilization. Stabilizationwas traditionally accomplished by filling the stone withnatural oils; however, modern synthetic resins such asOpticon are now being used. Resin filling is often morepermanent than the use of natural oils.Opals are oftenstabilized and emeralds have a long history of fracturefilling due to their popularity and a tendency to behighly fractured or contain multiple inclusions.S. The most controversial of all the modificationtechniques is the “creation”of gemstones.Culturedpearls are genuine but are created by using a center ofplastic or mother of pearl, rather than sand. Still apearl, just helped to grow by human intervention. Figure 1. Diamonds of varying color. Laboratory grown crystals of ruby, sapphire, diamond,emerald, and star sapphire are real semipreciousstones. They just weren't grown in the earth. So whatis the answer: Real or Fake? This argument can bediscussed with all sides being technically correct, but itis not the most important information. From a lapidaryor jeweler’s point of view, the most important topic isproper disclosure. Does the buyer know up front thatthe stone he is purchasing has been ‘helped along’bythe human touch? Gems are often examined by trained personnelusing optical microscopy and other methods. In somewell-studied cases like diamond, these techniques willusually suffice. However, imperfections can be readilyfilled with synthetic materials or the stone can beprocessed to alter the color and increase market value,with the unsuspecting consumer convinced that he haspurchaseda stone of greater value. With lessergemstones the analytical techniques are much lessestablished and more reliant on long experience withmineralogical identification methods. Ramanspectroscopy however provides an ideal method forthe examination of gemstones and semi-preciousstones. With the ability to microscopically examine bothloose and mounted stones, Raman can distinguish notonly real versus artificial gemstones, but can alsodiscriminate those that have been adulteratediraddition to providing details of the alteration. Gemstones loose and mounted in different types of14K gold jewelry settings (rings and pendants) werepurchased from various dealers. The gemstone wasthen placed into the sample compartment of a JASCOVentuno; a benchtop mounted,fully integrated confocalmicro-Raman spectrometer.The instrument wasequipped with a 532 nm diode laser; 2 gratings and anair cooled CCD detector. The integration times forspectral collection were 20 seconds per acquisition.The confocalaperture used(50mm), gives anapproximate 1mm (x,y) and 2mm (z) sample volume.The laser power at the sample was 10 mW or less. Results and Discussion Citrine is the most valuable Quartz gem. Almost allCitrine on the market is heat-treated Amethyst. NaturalCitrine is yellow to orange, and occurs in much lighterhues than the heat-treated material. In some Amethystdeposits, the Amethyst has been partially or fullychanged to brown Citrine by geothermal heating.Citrine may also be produced by heat-treating SmokyQuartz from certain localities. Citrine also closelyresembles topaz. Unfortunately, unscrupulous dealerslabel Citrine in such a way that unassuming buyersthink they are buying the more valuable topaz. Itshould be understood that any "Topaz" labeled with aprefix (such as Gold Topaz, Brazilian Topaz, andCitrine Topaz) is heat-treated Citrine. The Ramanspectra in Figure 2 clearly indicate the difference in thetwo gemstones. Figure 2. Citrine (blue), a(yellow-colored naturalquartz, can be passed off as the more expensive topaz(red) by unscrupulous gem dealers. All natural diamonds are “flawed", often by color orimpurities. Most diamonds have some yellow or browncolor. Defects mark the diamond as unique. Colorcenters in diamond photoluminesce (PL) when excitedby laser light. A Raman spectrometer used to measurePL is apowerful characterisation tool to identifyartificiallyreprocessed,,“exotic” coloreddiamonds.(Figure 3) The diamond grading system is as follows:D and F are colorless, G through J are near colorless,K through M are faint yellow or brown, N through Z arelight yellow, brown or grey, and Z's are fancy yellow orbrown. Figure 3. The 1332 cmdiamond band (red) alongwith the yellow 1576 cmPL emission (blue). The spectra of two other gemstones mounted asjewelry are shown in Figure 4. In these spectra thedifferences between the green peridot and the purpletanzanite are clearly identifiable. In conclusion Ramanis a powerful tool for the identification and qualificationof gemstones. Figure 4. The Raman spectra of peridot (green) andtanzanite (pink)
确定

还剩1页未读,是否继续阅读?
佳士科商贸有限公司为您提供《Raman 激光拉曼光谱仪鉴定宝石》,该方案主要用于珠宝/玉石中检测,参考标准--,《Raman 激光拉曼光谱仪鉴定宝石》用到的仪器有JASCONRS5000/7000共聚焦激光拉曼光谱仪、JASCORMP-500便携激光拉曼分光光度计、jascoRFT-6000傅立叶变换红外拉曼光谱仪
相关方案
更多











