
方案详情
文
This Application Note describes a method for the routine analysis of Stainless Steel samples.Fourteen trace elements, with a wide range of
concentrations, were determined using one sample preparation method.
方案详情

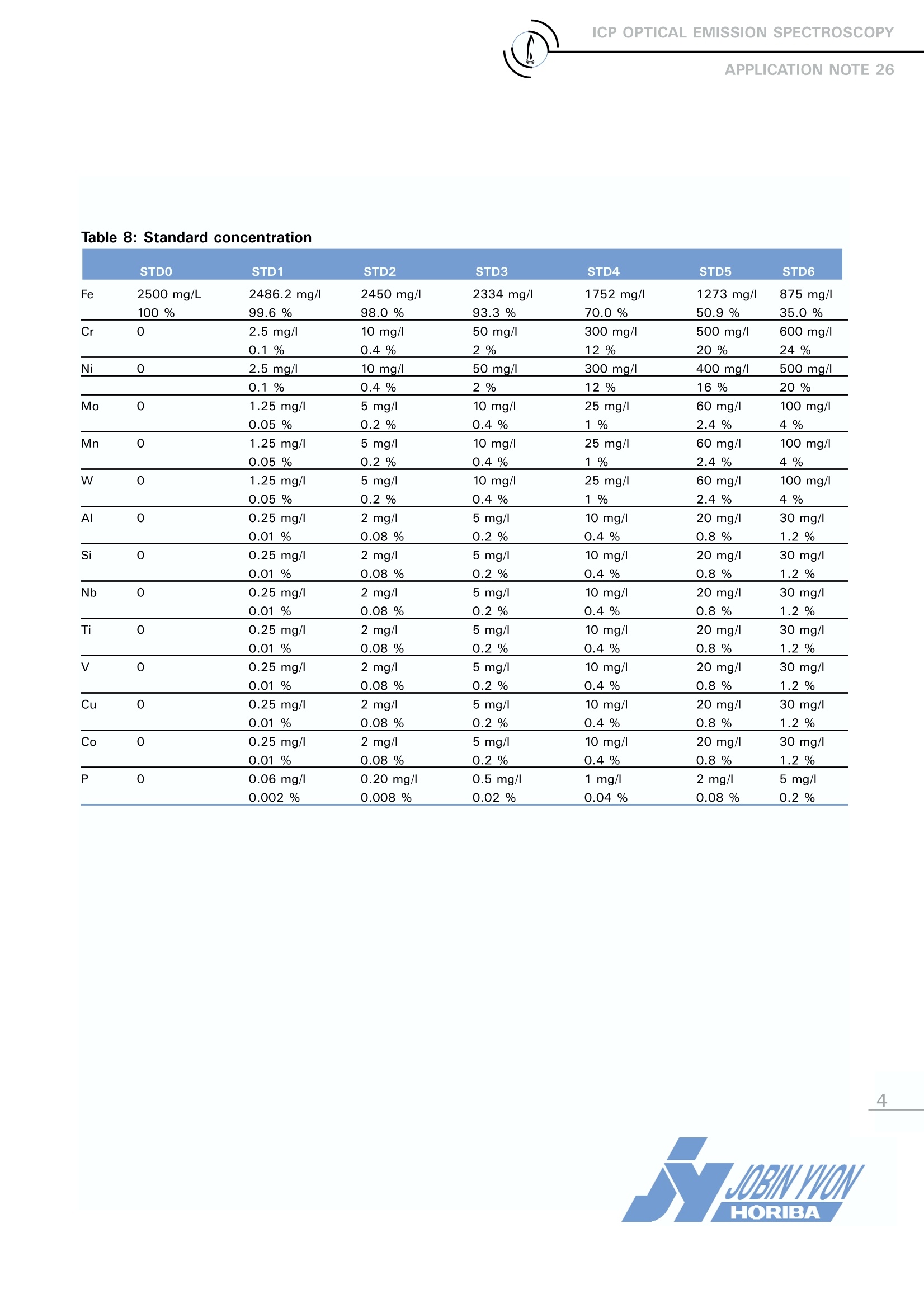
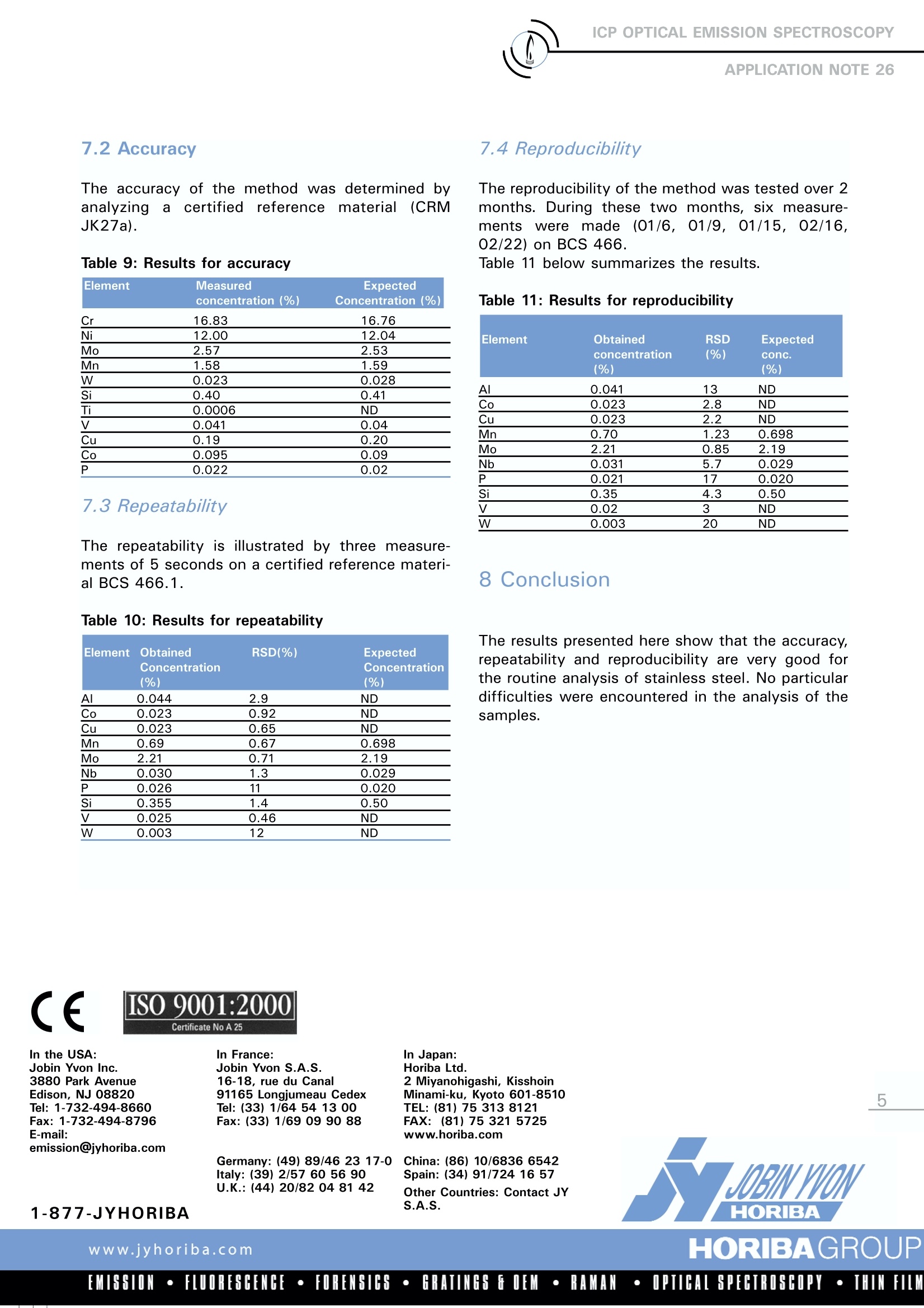
ICP OPTICAL EMISSION SPECTROSCOPYAPPLICATION NOTE 26 Analysis of 14 Trace Elements in Stainless Steel Joel Sire, Daniel Legain Serma Technologie France Keywords: metallurgy This Application Note describes a method for theroutine analysis of StainlesssSteeell samples.Fourteen trace elements, with a wide range ofconcentrations, were determined using one sam-ple preparation method. 2 Principle 2.1 Technique used The elemental analysis of these samples wasundertaken by Inductively CoupledPlasmaOptical Emission Spectrometry (ICP-OES).Thesample is nebulized then transferred to an argonplasma. It is decomposed, atomized and ionizedwhereby the atoms and ions are excited. Wemeasure the intensity of the light emitted whenthe atoms or ions return to lower levels of ener-gy. Each element emits light at characteristicwavelengths and these lines can be used forquantitative analysis after a calibration. 2.2 Wavelength choice The choice of the wavelength in a given matrixcan be made using the "profile" function, or byusing Win-IMAGE, which is rapid semi-quantita-tive analysis mode using multiple wavelengths.The principle is the same in either case: recordthe scans of analytes at low concentration, andof the matrix. By superimposing the spectra, wesee possible interferences. 3 Sample preparation 3.1 Required solutions Hydrofluoric acid 40% (d=1.13), Nitric acid 68% (d=1.4), Hydrochloric acid 36% (1.18), Ammonium phosphate,Single element standard solutions at 1 g/L ofAl, Co, Cu, Mn, Mo, Nb, P, Si, Ti, V, W,Iron powder (Johnson Matthey), Nickel and Chromium powder (Merck). Use six 250 mL PTFE beakers. Beaker STDO: Weigh, exactly, 1250 mg of Fe.Beaker STD1: Weigh, exactly, 1244.6 mg of Fe,1.25 mg of Cr and Ni. Beaker STD2: Weigh, exactly, 1225 mg of Fe, 5mg of Cr and Ni. Beaker STD3: Weigh, exactly, 1167 mg of Fe,25 mg of Cr and Ni. Beaker STD4: Weigh, exactly, 876 mg of Fe,150 mg of Cr and Ni. Beaker STD5: Weigh exactly 636.5 mg of Fe,250 mg of Cr and 200 mg of Ni. Beaker STD6: Weigh, exactly, 437.5 mg of Fe,325 mg of Cr and 250 mg of Ni. In each beaker, add 6.5 mL of HF then, withcare, 12.5 mL of HNO3 and 12.5 mL of HCI. Ifnecessary, heat on sand bath to finish the dis-.solution and let it cool.Transfer the solution tosix 500 mL PTFE flasks and follow the instruc-tions described below. Flask 1 (STDO): Dilute to volume with deionized water to obtaina solution of 2500 mg/L to be used as theblank sample. Flask 2 (STD1): Add 625 uL of the 1 g/L Mo, W and Mn stan-dard solutions. Add 1.25 mL of 0.1 g/L Al, Si, Nb, Ti, V, Cu,Co standard solutions. Add 300 uL of the 0.1 g/L P standard solutionDilute to volume with deionized water. Flask 3 (STD2): Add 2.5 mL of the 1 g/L Mo, W and Mn standard solutions.Add 1 mL of 1 g/L Al, Si, Nb, Ti, V, Cu, Co stan-dard solutions.Add 1.20 mL of the 0.1 g/L P standard solution. Dilute to volume with deionized water. Flask 4 (STD3): Add 5 mL of the 1 g/L Mo, W and Mn standard solutions.S.Add 2.5 mL of 1 g/L Al, Si, Nb, Ti, V, Cu, Costandard solutions.Add 250 uL of the 1 g/L P standard solution. Dilute to volume with deionized water. Flask 5 (STD4):Add 12.5 mL of the 1 g/L Mo, W and Mn stan-dard solutions.Add 5 mL of 1 g/L Al, Si, Nb, Ti, V, Cu, Co stan-dard solutions.Add 500 uL of the 1 g/L P standard solution. Dilute to volume with deionized water. Flask 6 (STD5): Add 30 mL of the 1 g/L Mo, W and Mn standardsolutions. Add 10 mL of 1 g/L Al, Si, Nb, Ti, V, Cu, Co stan-dard solutions. Add 1 mL of the 1 g/L P standard solution. Dilute to volume with deionized water. Flask 7 (STD6): Add 50 mL of the 1 g/L Mo, W and Mn standardsolutions. Add 15 mL of 1 g/L Al, Si, Nb, Ti, V, Cu, Co stan-dard solutions. Add 2.5 mL of the 1 g/L P standard solution.Dilute to volume with deionized water. 3.3 Sample preparation Weigh, exactly, 1g of sample to analyze. Add 5 mL of HF then add carefully 10 mL HNO3and 10 mL of HCI. Heat on a sand bath until thesample is dissolved and transfer to plastic 100 mLflask.Take care that the temperature does notexceed 55 °C to avoid the loss of Si during diges-tion of SiF6, which is volatile.e.Dilute to volumewith deionized water. A 10 g/L solution is obtained.Dilute it 4 times to obtain a 2.5 g/L solution, suit-able for analysis. 4. Instrument specification The work was done on a JY 80 instrument and isalso applicable to the JY 180 and ULTIMA 2CHRICP spectrometers. The specifications of this instru-ment are listed on the following page.The specifica-tions of this instrument are listed in Tables 1 to 3. Table 1: Specification of spectrometer: monochro-mator Parameters Specifications Mounting Czerny Turner Focal length 1m Nitrogen purge Yes Variable resolution Yes Grating number of grooves 3600 gr/mm Table 2: Specification of spectrometer: polychro-mator Parameters Specifications Mounting Paschen Runge Focal length 1m Nitrogen purge Yes Grating number of grooves 3000 gr/mm Table 3: Specification of RF Generator Parameters Specifications Type of generator Solid state Observation Radial Frequency 40.68 MHz Control of gas flowrate by computer Control of pump flow by computer Cooling air 5 Operating conditions The operating conditions are listed in Table 4 below. Table 4: Operating conditions Parameter Condition RF Generator power 1000 W Plasma gas flowrate 12 L/min Auxiliary gas flowrate O L/min Sheath gas flowrate 0.2 L/min Nebulizer flowrate 3.2 bars (48 psi) Sample uptake 1.8 mL/min Type of nebulizer Cross Flow Type of spray chamber Scott Argon humidifier Yes Injector tube diameter 3.0 mm 6 Wavelength selection and analyti-cal conditions For each element, the line with the highest sensi-tivity was used for analysis, because there were noproblems with interferences.FFor all the elementsthe conditions were the same. Table 5: Analytical conditions Element Slits Analysis Integration (um) mode time (sec) All elements 40x 20 Direct peaking 10 Table 6: Wavelengths used on the simultaneousspectrometer Element Wevelength (nm) Co 228.616 Cr 267.716 Cu 324.754 Fe 259.940 Mn 257.610 Mo 202.032 Nb 316.340 Ni 231.604 Si 251.611 Ti 337.279 V 310.230 W 207.911 Table 7: Wavelengths on the sequential spectrome-ter Element Wevelength (nm) AI 308.215 P 178.226 The normalization or 100% method was used. Thesum of the concentrations obtained is consideredto be equal to 100%. The calibration curve shouldbe undertaken with great care. This method canbe used for the analysis of all types of steel alloys. 7 Results 7.1 Calibration The standards prepared are shown in Table 8below. Table 8: Standard concentration STDO STD1 STD2 STD3 STD4 STD5 STD6 Fe 2500 mg/L 2486.2 mg/l 2450 mg/l 2334 mg/I 1752 mg/l 1273 mg/l 875 mg/l 100 % 99.6% 98.0% 93.3% 70.0% 50.9% 35.0% Cr 2.5 mg/l 10 mg/l 50 mg/l 300 mg/l 500 mg/l 600 mg/l 0.1% 0.4 % 2% 12% 20% 24% Ni 2.5 mg/l 10mg/ 50 mg/l 300 mg/l 400 mg/l 500 mg/l 0.1% 0.4% 2% 12% 16% 20% Mo 1.25 mg/l 5 mg/l 10 mg/I 25 mg/l 60 mg/l 100 mg/l 0.05% 0.2% 0.4% 1% 2.4% 4% Mn 0 1.25 mg/l 5 mg/l 10 mg/l 25 mg/l 60 mg/l 100 mg/I 0.05% 0.2% 0.4% 1% 2.4% 4% W 1.25 mg/l 5 mg/l 10 mg/l 25 mg/l 60 mg/l 100 mg/l 0.05% 0.2% 0.4% 1% 2.4% 4% Al 0 0.25 mg/ 2 mg/l 5 mg/l 10 mg/l 20 mg/l 30 mg/l 0.01% 0.08% 0.2% 0.4% 0.8% 1.2% Si 0 0.25 mg/l 2 mg/l 5 mg/1 10 mg/l 20 mg/l 30 mg/l 0.01% 0.08% 0.2% 0.4% 0.8% 1.2% Nb 0 0.25 mg/l 2 mg/l 5 mg/l 10 mg/l 20 mg/l 30 mg/l 0.01% 0.08% 0.2% 0.4% 0.8% 1.2% Ti 0.25 mg/l 2 mg/I 5 mg/l 10 mg/l 20 mg/l 30 mg/l 0.01% 0.08% 0.2% 0.4% 0.8% 1.2% V 0.25 mg/l 2 mg/l 5 mg/l 10 mg/l 20 mg/l 30 mg/l 0.01% 0.08 % 0.2% 0.4% 0.8% 1.2% Cu 0.25 mg/l 2mg/l 5 mg/l 10 mg/l 20 mg/l 30 mg/l 0.01% 0.08% 0.2% 0.4% 0.8% 1.2% Co 0.25 mg/l 2 mg/I 5 mg/l 10 mg/ 20 mg/l 30 mg/l 0.01% 0.08% 0.2% 0.4% 0.8% 1.2% P 0.06 mg/l 0.20 mg/l 0.5 mg/l 1 mg/l 2 mg/1 5 mg/ 0.002% 0.008% 0.02% 0.04 % 0.08% 0.2% 7.2 Accuracv The accuracy of the method was determined byanalyzingaacertified rreeffeerrence materialIe(CRMJK27a). Table 9: Results for accuracy Element Measured Expected concentration (%) Concentration(%) Cr 16.83 16.76 Ni 12.00 12.04 Mo 2.57 2.53 Mn 1.58 1.59 W 0.023 0.028 Si 0.40 0.41 Ti 0.0006 ND V 0.041 0.04 Cu 0.19 0.20 Co 0.095 0.09 P 0.022 0.02 7.3 Repeatability The repeatability is illustrated by three measure-ments of 5 seconds on a certified reference materi-al BCS 466.1. Table 10: Results for repeatability Element Obtained RSD(%) Expected Concentration Concentration (%) (%) AI 0.044 2.9 ND Co 0.023 0.92 ND Cu 0.023 0.65 ND Mn 0.69 0.67 0.698 Mo 2.21 0.71 2.19 Nb 0.030 1.3 0.029 P 0.026 11 0.020 Si 0.355 1.4 0.50 V 0.025 0.46 ND W 0.003 12 ND Element Obtained RSD Expected concentration (%) conc. (%) (%) AI 0.041 13 ND Co 0.023 2.8 ND Cu 0.023 2.2 ND Mn 0.70 1.23 0.698 Mo 2.21 0.85 2.19 Nb 0.031 5.7 0.029 P 0.021 17 0.020 Si 0.35 4.3 0.50 V 0.02 3 ND W 0.003 20 ND 8 Conclusion The results presented here show that the accuracy,repeatability and reproducibility are very good forthe routine analysis of stainless steel. No particulardifficulties were encountered in the analysis of thesamples. CE In the USA: Jobin Yvon Inc. 3880 Park Avenue Edison, NJ 08820 Tel:1-732-494-8660 Fax: 1-732-494-8796 E-mail: emission@jyhoriba.com Certificate No A 25 In France: In Japan: Jobin Yvon S.A.S. 16-18, rue du Canal 91165Longjumeau Cedex Tel: (33) 1/64 54 13 00 Fax: (33) 1/69 0990 88 Germany: (49) 89/46 23 17-0 Italy: (39) 2/57 60 56 90 Horiba Ltd. 2Miyanohigashi, Kisshoin Minami-ku, Kyoto 601-8510 TEL: (81)75 313 8121 FAX: (81)75 321 5725 www.horiba.com China: (86) 10/6836 6542 Spain: (34) 91/724 16 57
确定



还剩3页未读,是否继续阅读?
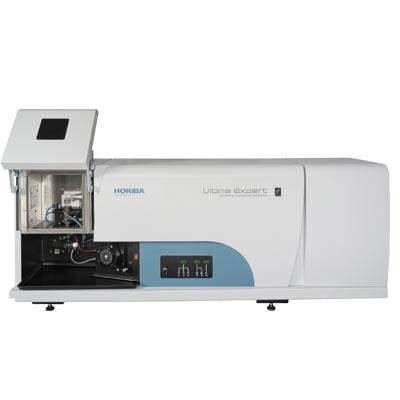
HORIBA(中国)为您提供《不锈钢中14种痕量元素的测定》,该方案主要用于合金中--检测,参考标准--,《不锈钢中14种痕量元素的测定》用到的仪器有HORIBA Ultima Expert高性能ICP光谱仪
相关方案
更多
该厂商其他方案
更多









