方案详情
文
Because biomarker concentrations decrease with increasing thermal maturity, light oils contain only a low concentration of detectable biomarkers, and in consequence require instrumentation of highest selectivity and sensitivity. The information of source, thermal maturity, and secondary alteration processes are furthermore often revealed by only subtle variations
in the isomeric distribution of such trace components. GC-MS/MS using the Thermo Scientific TSQ Quantum XLS is
the premier analytical method for the sensitive characterization of “molecular fossil” biomarkers in crude oil.
方案详情

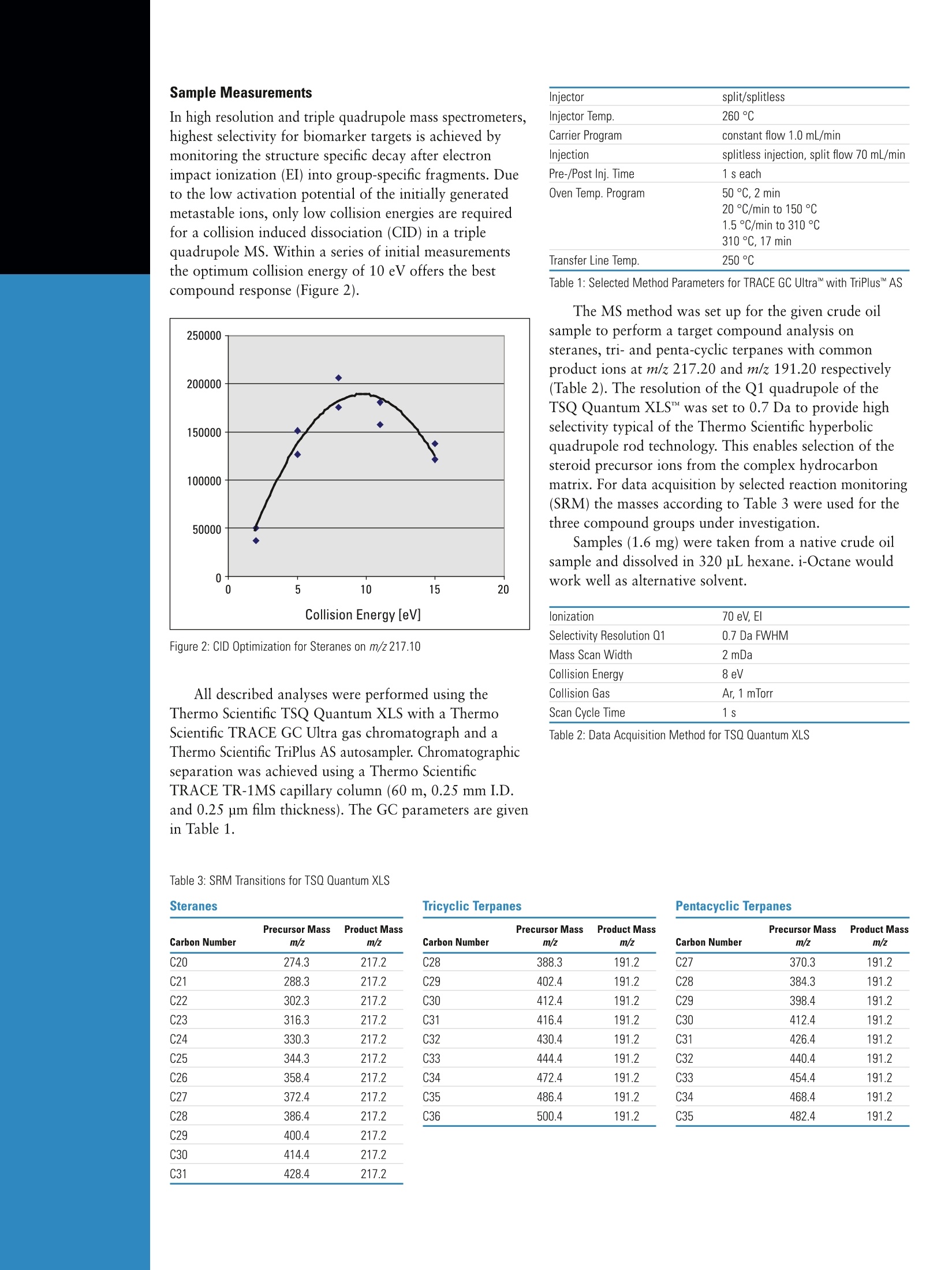
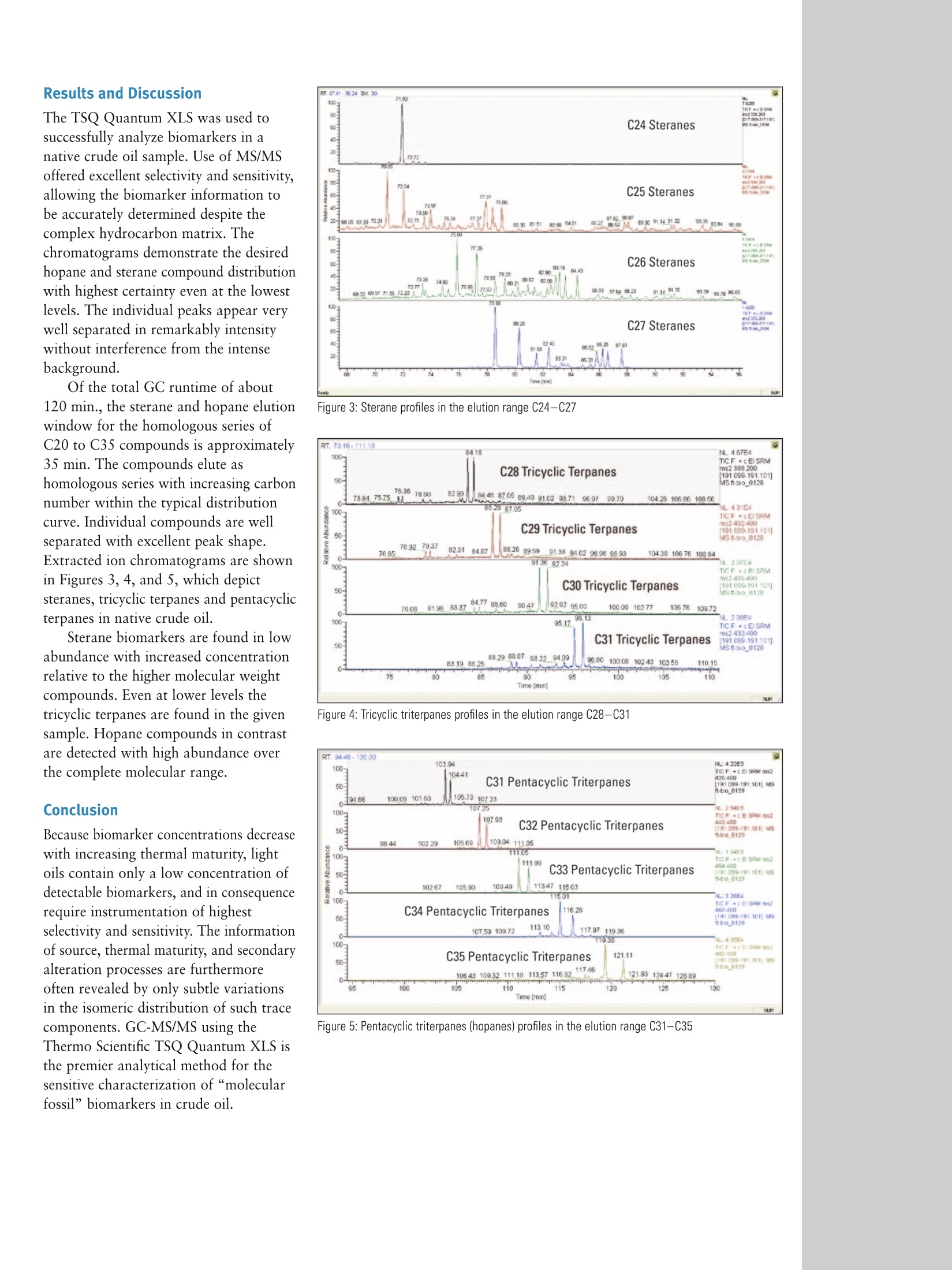
Part of Thermo Fisher Scientific Analysis of Molecular Fossils:Crude Oil Steroid Biomarker CharacterizationUsing Triple Quadrupole GC-MS/MS Frank Theobald, Environmental Consulting, Cologne, GermanyHans-Joachim Huebschmann, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Austin, TX, USA Introduction Due to the variety of geological conditions and ages underwhich oil was formed, every crude oil exhibits a uniquebiomarker fingerprint. Because of this, biological biomarkersare the most important hydrocarbon groups in petroleumbecause they can be used for chemical fingerprinting.Biomarkers reveal all or most of the original carbon skeletonof the original natural products.12 Relative to otherhydrocarbon components petroleum biomarkers are moreresistant to biodegradation but concentrations steadilydecrease as petroleum matures. The information frombiomarker analysis is used to determine the migrationpathways from a source rock to the reservoir, for thecorrelation of oils in terms of oil-to-oil and oil-to-sourcerock, the source potential, ranking of the relative thermalmaturity, as well as possible secondary alteration processes.Decisions for the commercial exploitation of a prospect arebased on that analytical background. Economics ultimatelydetermine if a petroleum reservoir is further developedand finally brought to the market.Refinery chemists aremostly interested in how oil behaves when feeding theprocesses into marketable products. Analyses ofpetrochemical biomarkers also have been proven useful inthe determination of petroleum-derived environmentalcontaminations.2 Biomarkers found in crude oils, rocks and sediments,also referenced as“molecular fossils" in the literature,demonstrate few or even no changes from their formerprecursor compounds: terpenoids (isoprenoids) and steroidsfound in the cells of the originating living organisms.24Biomarker concentrations in oils are low, typically in the lowppm and sub-ppm level in the presence of a highly complexpetroleum hydrocarbon matrix. As the concentrations ofbiomarkers in petroleum decrease with thermal maturity,oils of high maturity exhibit particular analyticalchallenges with only low biomarker concentrations.Highly selective, fast and sensitive mass analyzers as highresolution or triple quadrupole GC/MS instruments arecommon and required for meaningful biomarker analysis. Experimental Conditions Triple quadrupole mass spectrometry allows thedetermination of the structure related precursor-production relationships with significantly less matrix interferencethan single stage quadrupole MS. Based on the selectedreaction monitoring process (SRM) triple quadrupoletechnique provides a unique selectivity for biomarkerstudies. The analysis of sterane, tricyclic and pentacyclicterpanes (hopanes) biomarker have been subject to thedescribed application. The homologous series of sterane compounds in therange of C27-C30 produces in the collision cell of a triplestage quadrupole mass spectrometer under soft CIDconditions common product ions at m/z 217 from theindividual molecular ions ranging from m/z 274 to 428.Precursor ions of the hopane series in the range of C27-C35cover the molecular ion range of m/z 370 to 482. Eachof these precursor ions produces an intense product ionat m/z 191. For this application, chromatographic separation wasachieved using a 60 m apolar fused silica column, as isstandard in most laboratories. The temperature programis characterized with a low heating profile, which offersincreased chromatographic resolution especially for theseries of biomarker isomers. In high resolution and triple quadrupole mass spectrometers,highest selectivity for biomarker targets is achieved bymonitoring the structure specific decay after electronimpact ionization (EI) into group-specific fragments. Dueto the low activation potential of the initially generatedmetastable ions, only low collision energies are requiredfor a collision induced dissociation (CID) in a triplequadrupole MS. Within a series of initial measurementsthe optimum collision energy of 10 eV offers the bestcompound response (Figure 2). Figure 2: CID Optimization for Steranes on m/z217.10 All described analyses were performed using theThermo Scientific TSQ Quantum XLS with a ThermoScientific TRACE GC Ultra gas chromatograph and aThermo Scientific TriPlus AS autosampler. Chromatographicseparation was achieved using a Thermo ScientificTRACE TR-1MS capillary column (60 m, 0.25 mm I.D.and 0.25 pm film thickness). The GC parameters are givenin Table 1. Injector split/splitless Injector Temp. 260°℃ Carrier Program constant flow 1.0 mL/min Injection splitless injection, split flow 70 mL/min Pre-/Post Inj. Time 1 s each Oven Temp. Program 50 ℃, 2 min 20 °C/min to 150℃ 1.5°C/min to 310℃ 310℃, 17 min Transfer Line Temp. 250°C Table 1: Selected Method Parameters for TRACE GC UltraM with TriPlusAS The MS method was set up for the given crude oilsample to perform a target compound analysis onsteranes, tri- and penta-cyclic terpanes with commonproduct ions at m/z 217.20 and m/z 191.20 respectively(Table 2). The resolution of the Q1 quadrupole of theTSQ Quantum XLSM was set to 0.7 Da to provide highselectivity typical of the Thermo Scientific hyperbolicquadrupole rod technology. This enables selection of thesteroid precursor ions from the complex hydrocarbonmatrix. For data acquisition by selected reaction monitoring(SRM) the masses according to Table 3 were used for thethree compound groups under investigation. Samples (1.6 mg) were taken from a native crude oilsample and dissolved in 320 pL hexane. i-Octane wouldwork well as alternative solvent. lonization 70 eV, El Selectivity Resolution Q1 0.7 Da FWHM Mass Scan Width 2 mDa Collision Energy 8 eV Collision Gas Ar, 1 mTorr Scan Cycle Time 1 s Table 2: Data Acquisition Method for TSQ Quantum XLS Table 3: SRM Transitions for TSQ Quantum XLS Precursor Mass Product Mass Precursor Mass Product Mass Precursor Mass Product Mass Carbon Number m/z m/z Carbon Number m/z m/z Carbon Number m/z m/z C20 274.3 217.2 C28 388.3 191.2 C27 370.3 191.2 C21 288.3 217.2 C29 402.4 191.2 C28 384.3 191.2 C22 302.3 217.2 C30 412.4 191.2 C29 398.4 191.2 C23 316.3 217.2 C31 416.4 191.2 C30 412.4 191.2 C24 330.3 217.2 C32 430.4 191.2 C31 426.4 191.2 C25 344.3 217.2 C33 444.4 191.2 C32 440.4 191.2 C26 358.4 217.2 C34 472.4 191.2 C33 454.4 191.2 C27 372.4 217.2 C35 486.4 191.2 C34 468.4 191.2 C28 386.4 217.2 C36 500.4 191.2 C35 482.4 191.2 C29 400.4 217.2 C30 414.4 217.2 C31 428.4 217.2 Results and Discussion The TSQ Quantum XLS was used tosuccessfully analyze biomarkers in anative crude oil sample. Use of MS/MSoffered excellent selectivity and sensitivity,allowing the biomarker information tobe accurately determined despite thecomplex hydrocarbon matrix. Thechromatograms demonstrate the desiredhopane and sterane compound distributionwith highest certainty even at the lowestlevels. The individual peaks appear verywell separated in remarkably intensitywithout interference from the intensebackground. Of the total GC runtime of about120 min., the sterane and hopane elutionwindow for the homologous series ofC20 to C35 compounds is approximately35 min. The compounds elute ashomologous series with increasing carbonnumber within the typical distributioncurve. Individual compounds are wellseparated with excellent peak shape.Extracted ion chromatograms are shownin Figures 3, 4, and 5, which depictsteranes, tricyclic terpanes and pentacyclicterpanes in native crude oil. Sterane biomarkers are found in lowabundance with increased concentrationrelative to the higher molecular weightcompounds. Even at lower levels thetricyclic terpanes are found in the givensample. Hopane compounds in contrastare detected with high abundance overthe complete molecular range. Conclusion Because biomarker concentrations decreasewith increasing thermal maturity, lightoils contain only a low concentration ofdetectable biomarkers, and in consequencerequire instrumentation of highestselectivity and sensitivity. The informationof source, thermal maturity, and secondaryalteration processes are furthermoreoften revealed by only subtle variationsin the isomeric distribution of such tracecomponents. GC-MS/MS using theThermo Scientific TSQ Quantum XLS isthe premier analytical method for thesensitive characterization of“molecularfossil”biomarkers in crude oil. Figure 3: Sterane profiles in the elution range C24-C27 Figure 4: Tricyclic triterpanes profiles in the elution range C28-C31 Figure 5: Pentacyclic triterpanes (hopanes) profiles in the elution range C31-C35 ( 1. Wang, Z.; Yang, C.; et al. , Petro l eum Biomarker for Oil Spill Ch a racte r i z ation an d Source Ide n tif i cation, in: Wan g , Z .; Stout, S.; E d s: Oil Spill Environmental F orensics, A cadem i c P r ess: Oxford 2007. ) ( 2. Peters, K.E.; Moldowan, J.M., T h e Biomarker Guide: Interpreting molecular f o ssils i n petroleum and ancient sediments, Prentice Hall, New York, 1 39, ( 1 993) 3 63. ) ( 3. Hsu, C.;Walters, C .; et al., Biomarker Analysis in Petroleum Exploration, in: Hsu, C . S.; Ed. : Analytical Advances fo r Hydrocarbon Research,Springer: Berlin 2003. ) 4. Rullkoetter, J., Molekulare Fossilien, Nachr. Chem. Tech. Lab., 32 (1984)418-423. Legal Notices @2008-2010 Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc. All rights reserved. All trademarks are the property of Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc. and its subsidiaries. This information is presented as an example of the capabilities ofThermo Fisher Scientific Inc. products. It is not intended to encourage use of these productsin any manners that might infringe the intellectual property rights of others. Specifications, terms and pricing are subject to change. Not all products areavailable in all countries. Please consult your local sales representative for details. Due to the variety of geological conditions and ages under which oil was formed, every crude oil exhibits a unique biomarker fingerprint. Because of this, biological biomarkers are the most important hydrocarbon groups in petroleum because they can be used for chemical fingerprinting. Biomarkers reveal all or most of the original carbon skeleton of the original natural products.1,2 Relative to other hydrocarbon components petroleum biomarkers are more resistant to biodegradation but concentrations steadily decrease as petroleum matures. The information from biomarker analysis is used to determine the migration pathways from a source rock to the reservoir, for the correlation of oils in terms of oil-to-oil and oil-to-source rock, the source potential, ranking of the relative thermal maturity, as well as possible secondary alteration processes. Decisions for the commercial exploitation of a prospect arebased on that analytical background. Economics ultimately determine if a petroleum reservoir is further developed and finally brought to the market.3 Refinery chemists are mostly interested in how oil behaves when feeding the processes into marketable products. Analyses of petrochemical biomarkers also have been proven useful in the determination of petroleum-derived environmental contaminations.Biomarkers found in crude oils, rocks and sediments, also referenced as “molecular fossils” in the literature, demonstrate few or even no changes from their former precursor compounds: terpenoids (isoprenoids) and steroids found in the cells of the originating living organisms.2,4Biomarker concentrations in oils are low, typically in the low ppm and sub-ppm level in the presence of a highly complex petroleum hydrocarbon matrix. As the concentrations of biomarkers in petroleum decrease with thermal maturity, oils of high maturity exhibit particular analytical challenges with only low biomarker concentrations. Highly selective, fast and sensitive mass analyzers as high resolution or triple quadrupole GC/MS instruments arecommon and required for meaningful biomarker analysis.
确定

还剩2页未读,是否继续阅读?
赛默飞色谱与质谱为您提供《原油中甾烷,三环和五环萜烯检测方案(气相色谱仪)》,该方案主要用于原油中组成分析检测,参考标准--,《原油中甾烷,三环和五环萜烯检测方案(气相色谱仪)》用到的仪器有赛默飞TRACE 1300系列 模块化气相色谱仪、赛默飞TSQ Fortis™ 三重四极杆质谱仪、赛默飞Triplus 500 GC顶空自动进样器
相关方案
更多
该厂商其他方案
更多












