产地类别: 进口
看了气体流量计的用户又看了
燃烧是获得能量的一种主要方式,同时又是造成大气污染的重要因
素之一。使用Lavision公司的FlowMaster可以实时、在线的对火焰
成像,并且得到组分浓度、气体组成与火焰温度的定量信息。(激
光)汽缸内成像技术的发展在很大程度上推动了新的发动机技术的
出现(如直接注入技术和倾斜发动机)
Lavision的EngineMaster可以提供关于燃料准备情况、热点成像、
火焰传播、No形成和烟雾生成的有关信息
应用
> 研究火焰、燃烧炉/器、涡轮机、高压燃烧系统、化学反应器等燃
烧现象
> 研究点火现象, 激波管,汽油机、柴油机的内部燃烧现象.
测量能够给出的信息:
> OH*, CH*, C2*等成分的分布
火焰温度,火焰位置与稳定性
火焰前端位置及传播, 点火现象的发生
> 总气体浓度, 温度场
> 气体组成,燃料/空气混合, 温度
> 烟雾体积分数
> 燃料预燃情况, 尾气回收成像
> OH 形成, NO 产生,冲击效应
火焰中的自由基如:CH, CN, NH, CO, C2, NO2, SO2 等
性能
> 进行指定曲柄角分辨测量, 和曲柄角周期相关的统计分析
> 具有发动机同步接口
> 在一个曲柄角周期内的高速测量 (瞬态分析)
特殊应用和配置
> 在极小通光孔经情况下可以进行的内窥镜式(钥匙孔式)成像
> 用于火焰冷却的尾气再循环过程
> 玻璃器件成型所用火焰的性能分析
> CVD 过程控制:石英生产的火焰水解
> 应用于高压燃烧过程分析的激光诱导白炽光 (LII)技术
> 电荷分层现象的化学计量学 地图 (l-值)
可升级到:
SootMaster :用于 LII测量, SprayMaster 和 FlowMaster

德国LaVision PIV/PLIF粒子成像测速场仪
型号:FlowMaster® 150万 - 200万
水下粒子成像测速系统(Under Water PIV)
型号:FlowMaster®-UW 200万 - 300万
三维立体PIV
型号:FlowMaster® 3D 100万 - 120万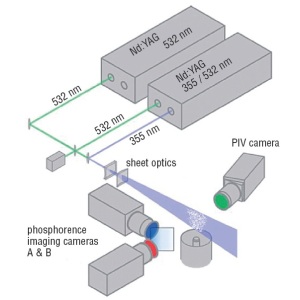
LaVision 热成像粒子成像测速系统(PIV)
型号:FlowMaster® thermographic 200万 - 300万Single-shot, tomographic imaging of the three-dimensional concentration field is demonstrated in a turbulent gaseous free jet in co-flow using volumetrically illuminated laser-induced fluorescence. The fourthharmonic output of an Nd:YAG laser at 266 nm is formed into a collimated 15 × 20 mm2 beam to excite the ground singlet state of acetone seeded into the central jet. Subsequent fluorescence is collected along eight lines of sight for tomographic reconstruction using a combination of stereoscopes optically coupled to four two-stage intensified CMOS cameras. The performance of the imaging system is evaluated and shown to be sufficient for recording instantaneous three-dimensional features with high signal-tonoise (130:1) and nominal spatial resolution of 0.6–1.5 mm at x/D = 7–15.5.
This paper describes the development of an experimental technique that combines simultaneous planar laser-induced fluorescence (PLIF) and infrared (IR) thermography imaging, and its application to the measurement of unsteady and conjugate heat-transfer in harmonically forced, thin liquid-film flows falling under the action of gravity over an inclined electrically heated-foil substrate. Quantitative, spatiotemporally resolved and simultaneously conducted measurements are reported of the film thickness, film free-surface temperature, solid–liquid substrate interface temperature, and local/instantaneous heat flux exchanged with the heated substrate. Based on this information, local and instantaneous heat-transfer coefficients (HTCs) are recovered. Results concerning the local and instantaneous HTC and how this is correlated with the local and instantaneous film thickness suggest considerable heat-transfer enhancement relative to steady-flow predictions in the thinner film regions.
The ignition characteristics of a premixed bluff-body burner under lean conditions were investigated experimentally and numerically with a physical model focusing on ignition probability. Visualisation of the flame with a 5 kHz OH* chemiluminescence camera confirmed that successful ignitions were those associated with the movement of the kernel upstream, consistent with previous work on non-premixed systems. Performing many separate ignition trials at the same spark position and flow conditions resulted in a quantification of the ignition probability Pign, which was found to decrease with increasing distance downstream of the bluff body and a decrease in equivalence ratio. Flows corresponding to flames close to the blow-off limit could not be ignited, although such flames were stable if reached from a richer already ignited condition.
不断发展的工业和快速成长的全球化市场对初级能源供应的增加,可靠的本地化制造和灵 活的公共交通运输都提出了与日俱增的需求。 尽管可替代技术方兴未艾并日益获得关注,但传统的、通过燃烧获得动力的途径在未来数 十年内仍将在能源结构中占有重要份额(参考下面“世界能源展望”图表)。 伴随可再生能源日益强烈的冲击,产生动力和热量的燃料种类的多样性也得到了空前规模 的扩展。此外,对能源利用效率和燃烧生成污染物控制的立法在逐步强化。对燃烧相关的 复杂过程的深入而细致的理解将会促进相关测量技术的进步。而这将有助于应对当前能源 领域的挑战并为未来发展储备所需技术。
LaVision GmbH气体流量计PLIF-FlameMaster的工作原理介绍
气体流量计PLIF-FlameMaster的使用方法?
LaVision GmbHPLIF-FlameMaster多少钱一台?
气体流量计PLIF-FlameMaster可以检测什么?
气体流量计PLIF-FlameMaster使用的注意事项?
LaVision GmbHPLIF-FlameMaster的说明书有吗?
LaVision GmbH气体流量计PLIF-FlameMaster的操作规程有吗?
LaVision GmbH气体流量计PLIF-FlameMaster报价含票含运吗?
LaVision GmbHPLIF-FlameMaster有现货吗?
最多添加5台
