发酵系统在曲霉菌培养中的应用
2023/03/03 13:33
阅读:94
分享:方案摘要:
产品配置单:
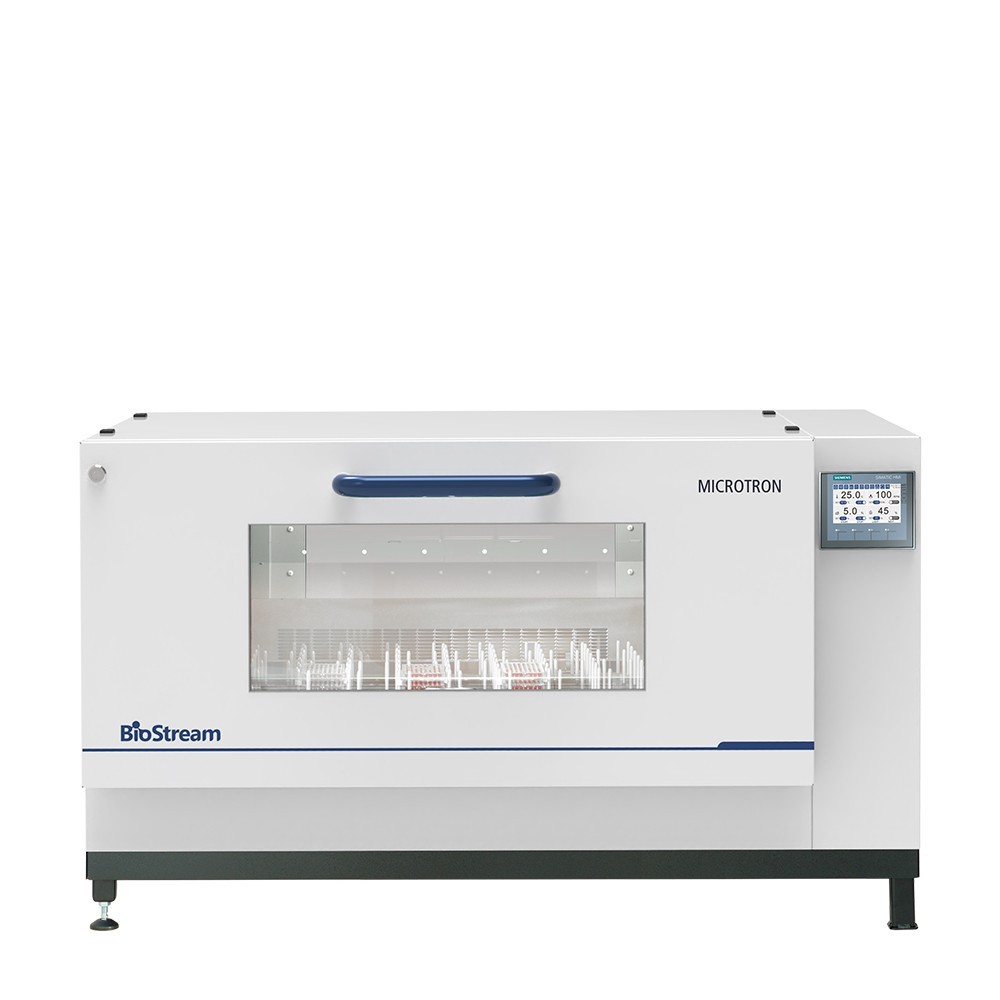
博奥思 Microtron 高速振荡培养箱
型号: Microtron
产地: 荷兰
品牌: 博奥思
¥30万 - 45万
参考报价
联系电话
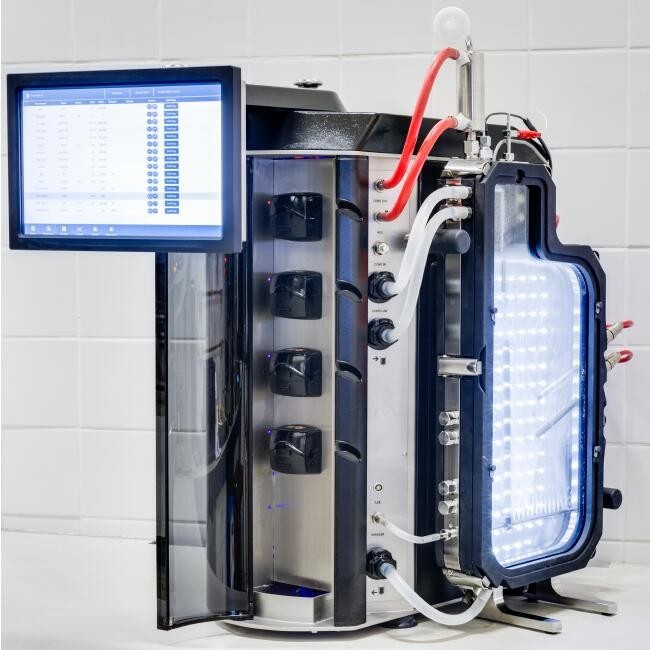
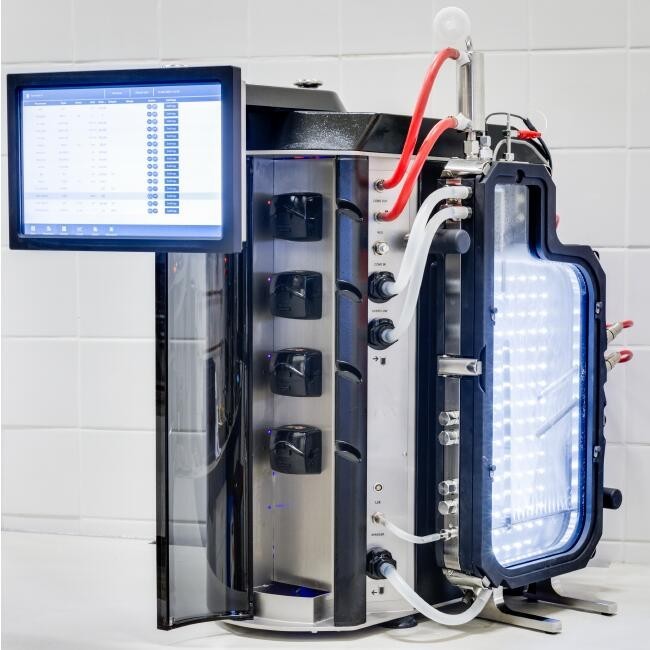
博奥思 BioBench Lux 平板LED光照反应器
型号: BioBench Lux
产地: 荷兰
品牌: 博奥思
¥35万 - 55万
参考报价
联系电话
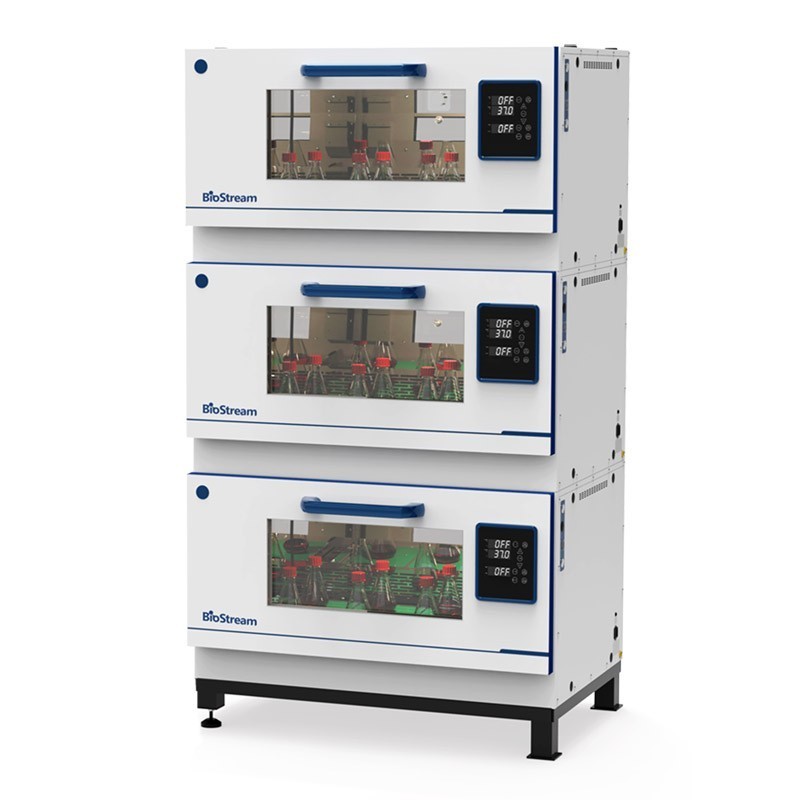
博奥思 B3/B5/B7 通用振荡培养箱
型号: B3/B5/B7
产地: 荷兰
品牌: 博奥思
¥10万 - 30万
参考报价
联系电话
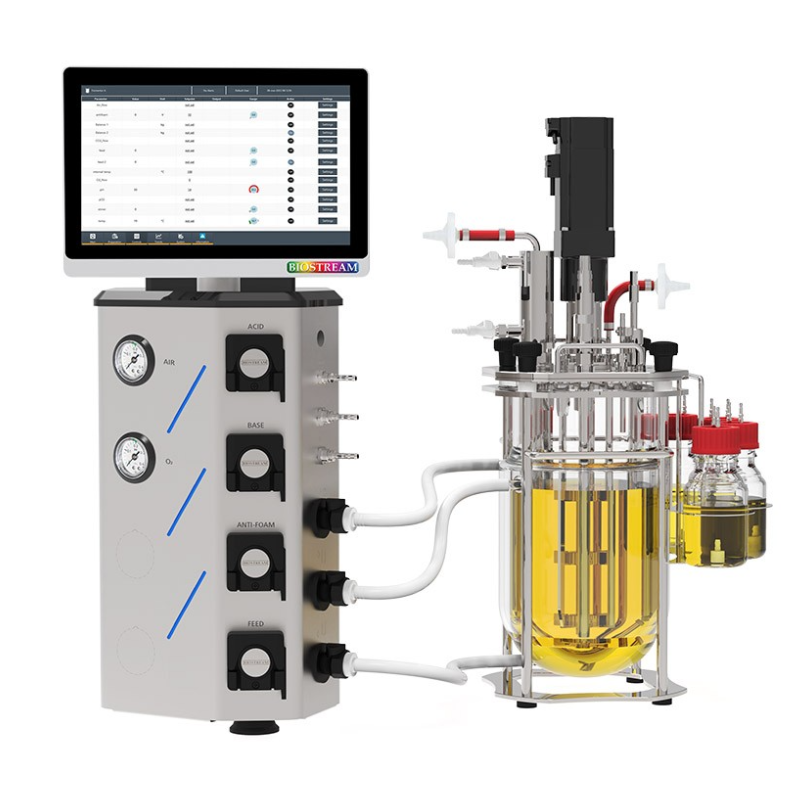
博奥思 BioUniv 台式生物反应器
型号: BioUniv
产地: 荷兰
品牌: 博奥思
¥20万 - 30万
参考报价
联系电话
博奥思 CRC CO2培养箱用振荡器
型号: CRC
产地: 荷兰
品牌: 博奥思
¥1
参考报价
联系电话
博奥思 Vdose Elite 蠕动泵
型号: Vdose Elite
产地: 荷兰
品牌: 博奥思
¥4万 - 5万
参考报价
联系电话
博奥思 C7/C5/C3 多功能细胞培养振荡培养箱
型号: C7
产地: 荷兰
品牌: 博奥思
¥20万 - 60万
参考报价
联系电话
方案详情:
发酵系统在曲霉菌培养中的应用
曲霉菌在自然界广泛分布,可感染动物,也可寄生于饲料、粮食中引起动物中毒。常见有烟曲霉、黄曲霉、寄生曲霉、棕曲霉、杂色曲霉、构巢曲霉、白曲霉以及黑曲霉等,其中以烟曲霉感染致病为主,同时也可产生毒素,黄曲霉、寄生曲霉、棕曲霉、杂色曲霉等主要均以所产毒素而致病。
曲霉的菌丝分支分隔,分生孢子梗生长在足细胞上,不分支。顶端膨大呈圆形的顶囊,上着许多单层或双层的小梗,小梗着生分生孢子,孢子呈链状,可呈黄、绿、黑、灰等颜色。
The fermenter is supplied in a configuration to provide an excellent bioreactor for this purpose.
* Powerful, top drive system with lubricated mechanical seal (magnetic options for Techfors)
* Jacketed system for efficient heat transfer.
* High-accuracy pumps for addition of pH control reagents, antifoam and feed (option on some units)
* Control of dissolved oxygen by stirrer speed as standard (air flow, pressure & oxygen, supplement options)
* Optional analogue feed pump for variable speed additon
* Analogue input/output for addition of external pumpsand sensros for eg. OD
Vessels:
All vessels are stainless steel (1.4435) with a dished base and top plate in several standard sizes. Temperature control can be by water circulation with either a heating element or steam injection into a pocket/exchanger.
All vessels are with a mechanical seal drive (magnetic coupling for cells). The drive shaft has a simple and secure connection for the motor. The top plate is equipped with 10mm, PG13.5 and standard, rounded -thread 19mm ports which can be fitted with a septum and retaining collar to allow flaming of the port during inoculation etc. (number and type varies according to specific fermenter). Bottom ports are 25mm Ingold standard and numbers vary by size.
The vessels are sterilized in situ (Techfors and Techfors S) with automatic sequencing. Reagent bottles and inlet pipes etc are usually autoclaved separately (options & alternatives, depending on size and configuration)..
Stirring
The fermenter has a powerful brushless motor with integral speed controller for speeds from 100 - 1500 rpm, depending on the vessel size and number of impellors. Powerful fluid cooled motors are standard for Techfors.
x-DDC Control System:
All fermenter models except Minifors incorporate the x-DDC (eXtended DDC microprocessor control) which uses a high-performance digital system. With the use of almost identical instrumentation, the step from Bench-scale to larger equipment is made considerably easier.
The control panel is compact and is usually mounted above the base unit for clear visibility. The panel can be removed if required. Programming of parameters is via a splashproof keypad with a rotary knob for navigation and an LCD display. Communication is via a robust data-cable. For each fermenter, process information such as parameter set points, PID values etc are stored automatically on an interchangeable "memory card" . This allows changes in fermentation processes by fitting an alternative card or downloading a recipe without re-programming and the chance of errors plus an unlimited number of recipes to be stored.
An "open frame" gas supply system with four magnetic valves allow addition of components for automatic mixing of gasses for oxygen supplementation. An optional mass flow control valve ensures a controlled, steady flow of gas into the vessel. Agitation & temperature control. Four high-accuracy digital peristaltic pumps supplied as standard with the option to add an integral analogue feed pump. Addition and removal of liquids is therefore possible with a standard system (using the antifoam pump for medium take-off). Accepts a conductive probe for automatic control of antifoam addition or media addition/removal in a vessel. Works together with the integral peristaltic pumps.
Set points and control strategies
Set points are entered into the controller prior to inoculation and stored on a memory card (except Minifors). The vessel was allowed to equilibrate prior to inoculation. The pO2 actual value may stay above the set point up to (and some times after) inoculation.
Temperature:28-32°C
pH:5-5.6
DO:30%
Agitation:600 rpm+ .
O2 :Optional supplementation of the air stream using a magnetic valve (rotameter)
PH Control
The pH probe is calibrated prior to the autoclave cycle (refer to fermenter Instruction Manual). pH control parameters are:
Base: 2M NaOH
Acid: 2M H3PO4
Transfer tubing :Narrow bore silicone tubing with Marprene insert, as supplied (4mm OD)
Vessel inlet :4mm fixed pipes in the vessel top plate
PID values: factory default setting should be used unless it is clear adjustment is needed (hunt or drift).
Dissolved Oxygen (pO2) Control
The dissolved oxygen electrode 100% is normally calibrated after the autoclave cycle (refer tto Instrucion Manual) but can be calibrated in air beforehand for cell culture applications. Control of pO2 can be cascaded eg rpm, airflow, gasmix (depending on options and fermenter type). The controller automatically maintains the pO2 setpoint. The gas flow rate should be set at a fairly low rate initially eg. 0.3 vessel volumes per minute (VVM) and raised incrementally during the fermentation to 1VVM (max. 1.5-2 VVM) whenever the stirrer cannot maintain the correct pO2 value (usually required within an hour or so).
Fed-batch/Continuous Feed
Feed pumps can be calibrated using the standard tubing to keep track of the liquid quantities entering and exiting the vessel. Either a digital pump with shot and delay dosing or an analogue, continuously-variable pump can be used for medium addition. Samples should be taken several times a day to measure parameters such as cell numbers, viability, carbon-source concentration etc). Iris v5 software can be used to control nutrient addition. Fed-batch does not involve removal of liquid.
Feeding can be related to dissolved oxygen concentration by using software control sequences.
Foam Control
This can be achieved by adding a small quantity of antifoam into the medium before inoculation (eg. 0.005 -0.01%) and subsequently controlled by a liquid antifoam delivered on demand into the vessel (or at regular time intervals). An antifoam probe uses conductivity to detect the presence of foam. The clear sheathing around the probe should not be damaged or false positive readings will occur.
Example methodology
Medium
Molasses or YPG medium plus supplements. Use of antifoam in the medium can help suppress foaming. Supplements are filter sterilized and added after sterilization of the bulk medium in the vessel (10% loss of volume is typically experienced during the sterilization process; allow for this).
Inoculum
Prepared in an Infors shaker (Minitron or Multitron) from a 24 hour culture of spores inoculated into 250ml shake flasks containing 50ml of medium. Shaker speed is 240rpm and a temperature 32oC. Use these to inoculate the fermenter as a 5%.by volume concentrate of actively growing cells.
Method
Electrodes should have been calibrated before autoclaving (pH and zero point pO2).• Sterilize the vessel with the basic medium. Adjust for evaporation losses, if necessary.
• Allow to cool to operating conditions and then calibrate pO2 100% value.
• Add any supplements then inoculate using a syringe or transfer line. Take a To sample for pH, optical density and glucose measurement. Dry weight values can be related to optical density readings and total/viable counts as required. Sample at eg. 1 hour intervals to follow the process.
After a lag phase of several hours a strong logarithmic growth should occur with substrate depletion unless fed-batch or continuous operation is implemented. The end of active growth may be marked by a rise in the dissolved oxygen concentration/decrease in stirrer speed. Typically, fermentations last up to 7 days.
Aspergillus species are a diverse group, so only general guidelines can be provided as a starting point.
下载本篇解决方案:
更多![]()
振荡在生物培养中的作用
生物培养分为静态培养和振荡培养。振荡培养,亦称悬浮培养,是指把微生物细胞接种于液体培养基中,并放置在摇床或振荡器上不停振荡的一种培养方法。广泛应用于菌种筛选和微生物扩大培养,是微生物生理、生化、发酵和其他生命科学研究领域中常用的培养方式。振荡培养不适用于含有易挥发性化学溶剂,低浓度爆炸气体和低燃点气体的物质以及有毒物质的培养。
生物产业
2023/07/28
箱体分舱段,培养条件更稳定
二氧化碳培养箱是通过在培养箱箱体内模拟形成一个类似细胞/组织在生物体内的生长环境,培养箱要求稳定的温度(比如哺乳动物为37°C)、稳定的CO2水平(一般为5-7%)、恒定的酸碱值(pH值一般为7.2-7.4)、较高的湿度,是细胞、组织、细菌培养的一种仪器,是开展免疫学、肿瘤学、遗传学及生物工程所必须的关键设备。
生物产业
2023/07/26
为什么细胞培养需要二氧化碳?
CO2既是细胞代谢产物,也是细胞所需成分,它主要与维持培养液的pH有直接关系。动物细胞多数需要微碱性环境,pH为7.2~7.4,以不超出6.8~7.6为宜。在细胞培养过程中,随着CO2释放量的增多,培养基会变酸,因此常加入NaHCO3(与CO2溶于水后所形成的H2CO3构成一个缓冲对)来调节pH,以保持培养液中溶解的二氧化碳的浓度。同时细胞培养的器皿需要一定程度的透气,以便于气体的交换。
生物产业
2023/07/26